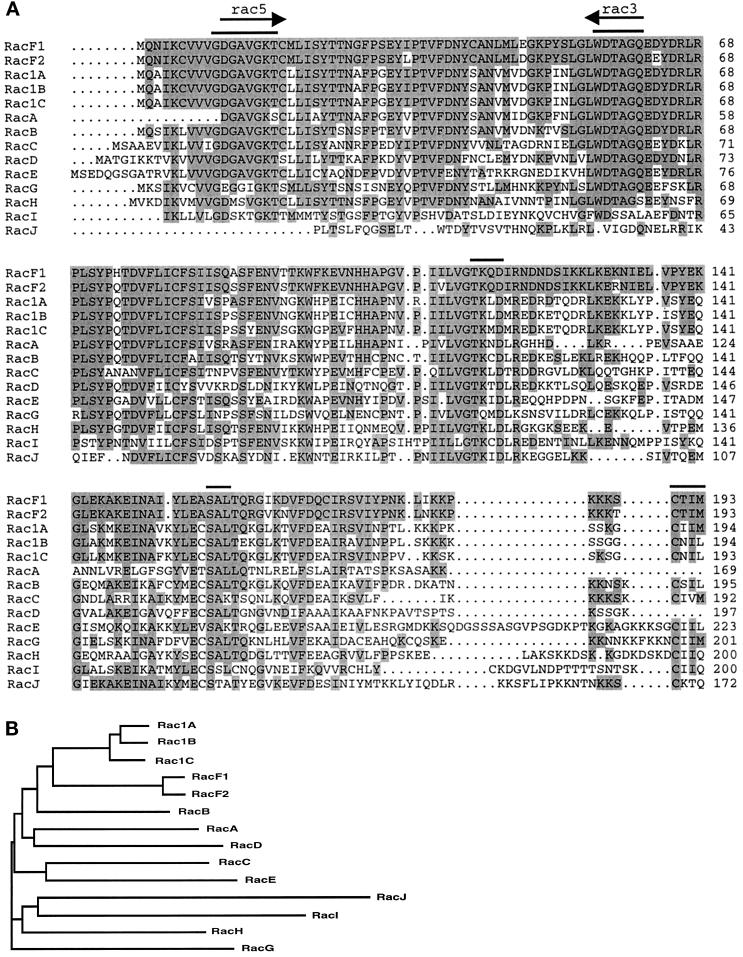
Figure 2.
(A) Alignment of RacF1 with members of the Rac subfamily in Dictyostelium. Residues that are identical between RacF1 and any of the other members of the Rac subfamily are shadowed. Arrows indicate the sequences used to design the degenerate primers for cloning the racF1 gene. Bars indicate conserved functional elements discussed in the text. GenBank accession numbers: RacF1, AF037042; RacF2, C94218; Rac1A, L11588; Rac1B, L11589; Rac1C, L11590; RacA, L11591; RacB, L11592; RacC, L11593; RacD, L11594; RacE, U41222; RacG, C92890; RacH, C92764; RacI, C84883; RacJ, C91054. Sequences corresponding to RacG, RacH, RacI, and RacJ, as well as the amino termini of Rac1C and RacD, were found after screening of the Dictyostelium sequence databank of the Japanese cDNA sequencing project (University of Tsukuba, Japan). (B) Phylogenetic analysis of the Dictyostelium Rac subfamily. The sequences most related to that of RacF1 and RacF2 are those from Rac1A, Rac1B, Rac1C, and RacB. Sequences were aligned using the Clustal W program (Wisconsin Package version 9.0), and the phylogenetic tree was displayed using TreeView (Institute of Biomedical and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom).