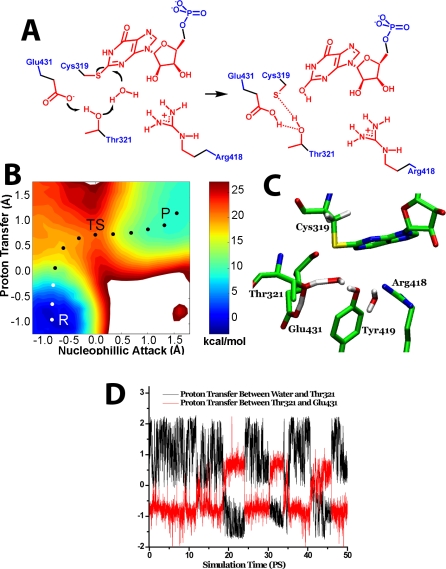
Figure 4. Simulation of the Thr321 Pathway.
(A) The hydrolysis of E-XMP* with Thr321 acting as the general base catalyst. Color key as described above.
(B) The free energy landscape of the Thr321 pathway, with axes as described above, except that the second proton acceptor is the OH of Thr321. As above, proton transfer is virtually complete at the transition state, whereas nucleophillic attack has just reached the reaction midpoint. P, product; R, reactant; TS, transition state.
(C) The corresponding transition state structure.
(D) The correlation between proton transfer from water to Thr321 and proton transfer from Thr321 and Glu431. Atoms treated as described in Figure 1. The reaction coordinate for the proton transfer between water and Thr321 was set as the distance traversed by the proton as it moves between the oxygen of water to the oxygen of Thr321; the reaction coordinate for the proton transfer between Thr321 and Glu431 was set as the distance traversed by the proton that moves between the oxygen of Thr321 and the oxygen of Glu431.