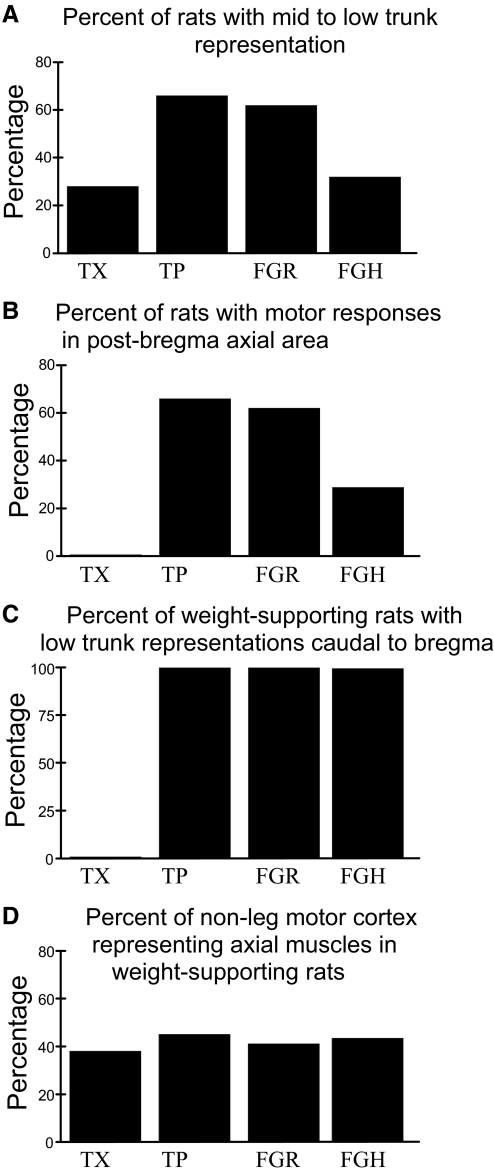
FIG. 3.
Organization of rats spinalized but achieving hindlimb weight support. A: percentage of rats with each treatment possessing specific mid- to low-trunk motor representation in cortex. The percentages match exactly those in Fig. 1. B: percentage of all rats with each treatment representing mid-to-low trunk behind bregma. C: percentage of weight-supporting rats representing mid-to-low trunk behind bregma. No TX rats possess motor representations in the normal hindlimb trunk area. All weight-supporting rats in TP, FGR, and FGH groups do. D: percentage of ICMS responsive cortical area devoted to trunk control was statistically indistinguishable in the treatment groups. This percentage of cortex also resembles the intact rat percentage of cortex after pure hindlimb areas of representation are removed from consideration (not shown).