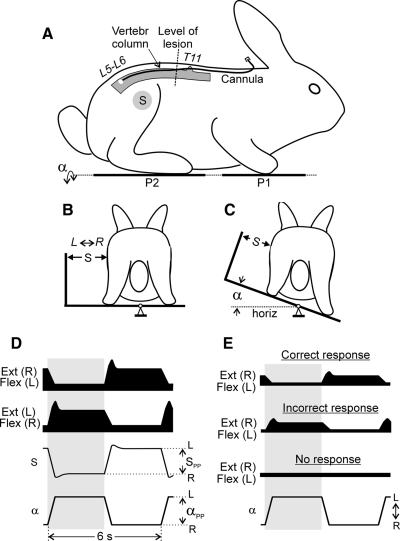
FIG. 1.
Experimental design and postural responses to tilts. Position of the cannula for drug administration and the level of spinal cord damage are shown in A. A–C: testing of postural responses to tilts. The animal was standing on 2 platforms: 1 under the forelimbs (P1) and 1 under the hindlimbs (P2). Platform P2 could be tilted in the transverse plane (α is the platform tilt angle). The sagittal plane of the animal was aligned to the axis of platform rotation. Mechanical sensor S, positioned at the half-height of the body, measured lateral displacements of the caudal part of the trunk in relation to the P2 platform. D: schematic representation of the trajectory of the platform angle (α), corrective movements of the caudal trunk (S), and EMG responses in right (R) and left (L) flexor (Flex) and extensor (Ext) limb muscles. The following values were measured: αPP, the peak-to-peak value of tilt angle of the P2 platform; SPP, the peak-to-peak value of postural corrections in the hindquarters. E: types of EMG responses in the right extensor and left flexor muscles observed in ventral hemisection (VHS) or ventral quadrant (VQ) animals: (i) correct response (Ext EMG is timed to the ipsilateral tilt, and Flex EMG to the contralateral tilt); (ii) incorrect response (opposite phase relations); (iii) no response.