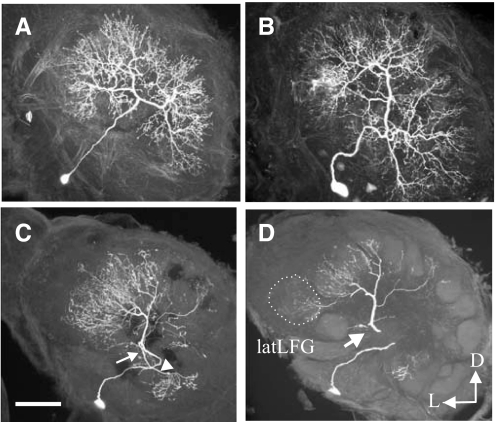
FIG. 6.
Examples of morphological types of local interneurons (LNs) in the ALs of female M. sexta. LNs are confined to the ALs. A: this type of LN exhibits a symmetrical arborization pattern in which the dendrites branch radially from the major neurite in the central, coarse neuropil and ramify widely in the glomeruli. B: this type of LN is distinguished by the marked asymmetry in the branching pattern of their neurites into the glomeruli and also ramifies widely in the glomeruli. C and D: this type of LN shows an asymmetric pattern, but the arborizations are limited to a smaller number of glomeruli. D: confocal microscopic image obtained from the neuron shown in C after embedding in plastic and sectioning. This neuron had 2 main neurites, one connecting a large number of glomeruli (C and D, →), which includes the latLFG (D, ···), and the other connecting fewer glomeruli (C, ▵). Scale bars: 100 μm. This figure illustrates the different types of LNs that mediate interglomerular interactions. The different morphologies provide a neuronal substrate for proposed global and glomerulus-specific inhibitory networks (Silbering and Galizia 2007).