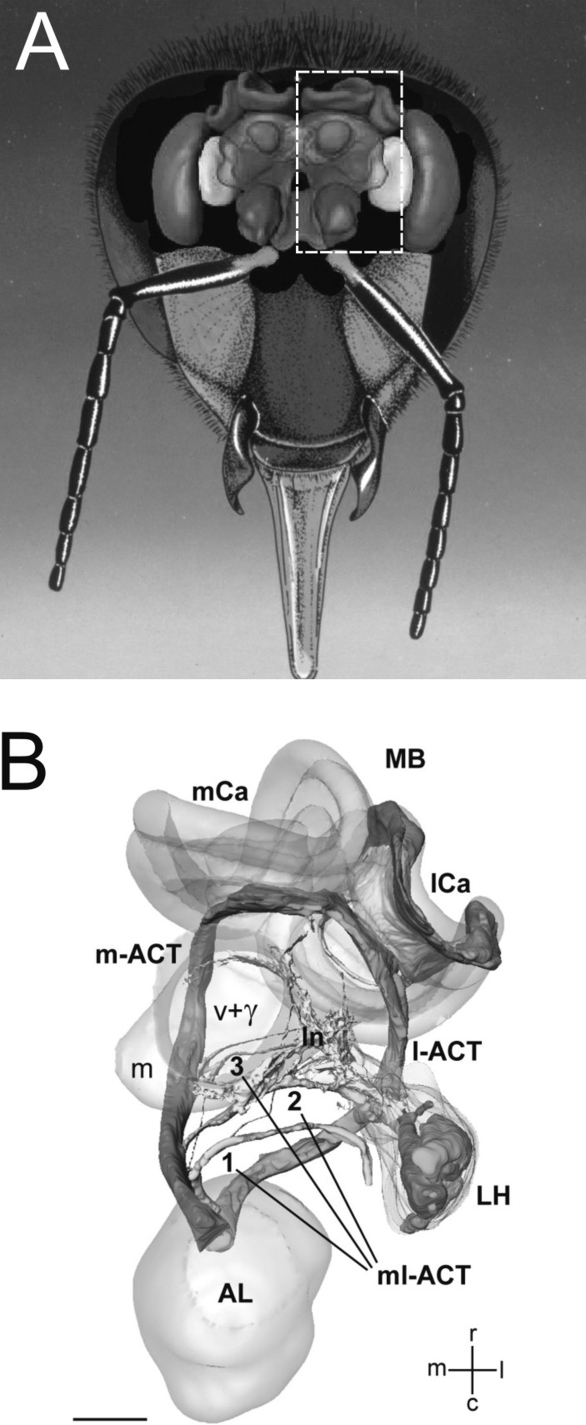
Figure 2.
The basic organization of the honeybee olfactory system. (A) Frontal view of the brain with the main olfactory centers. (B) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the olfactory circuit based on confocal microscopy (corresponding to the bees' left half-brain, see broken line in (A); AL: antennal lobe; LH: lateral horn; MB: mushroom body; m-ACT: medial antenno-cerebral tract; l-ACT: lateral antenno-cerebral tract; mCa: medial calyx; lCa: lateral calyx. The three ml-ACTs (mediolateral antenno-cerebral tracts) 1–3 branch off the m-ACT sequentially and innervate the lateral protocerebral lobe to form the lateral network (ln) that spans from the vertical lobe (v + γ) to the LH. Scale bar: 100 μm (Figure 3B adapted from Kirschner et al., 2006 by kind courtesy of Wolfgang Rössler).