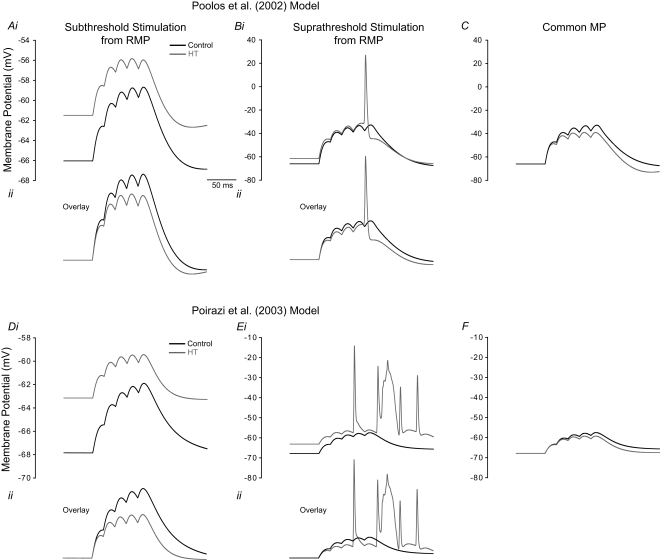
Figure 4.
Model HT cell shows reduced EPSP summation but increased firing than control due to depolarized RMP. (A–C) refer to simulations performed using the Poolos et al. (2002) model, and (D–F) are simulations using the Poirazi et al. (2003) model. (Ai, Di) Train of five small EPSPs from the RMP in control (black) and HT (grey) model cells. (Aii, Dii) Overlay of the traces in (Ai, Di) showing decreased EPSP summation in the HT model cells. (Bi, Ei) Train of five large EPSPs, resulting in AP firing in the HT model cells (grey), but not in controls (black). (Bii, Eii) Overlay of the traces in (Bi, Ei). (C, F) Train of five large EPSPs in control (black) and HT (grey) model cells, from a common holding potential. Note that compensation of the depolarized RMP in the HT model cells eliminates AP firing.