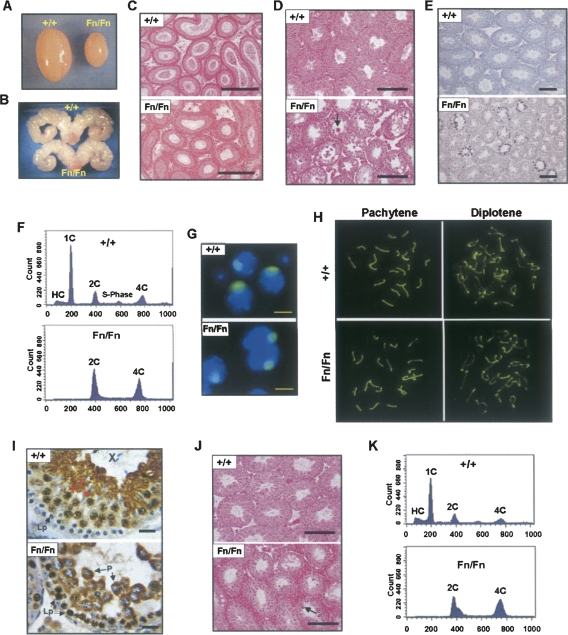
FIGURE 4.
Spermatogenic defects in adult male Dazap1Fn/Fn mice. The animals were 5–7 wk old in A-I and 1 yr old in J and K. (A) The testes. (B) The seminal vesicles. (C) H&E staining of epididymis sections. (D,J) H&E staining of testis sections. The arrows point to multinucleated giant cells. (E) TUNEL staining of apoptotic cells on testis sections. (F,K) FACS profiles of testis cells sorted according to their DNA contents. Cell types in the various peaks are (HC) hypo-stained elongating and elongated spermatids; (1C) round spermatids; (2C) spermatogonia, secondary spermatocytes, and somatic cells; (S-phase) spermatogonia synthesizing DNA; and (4C) primary spermatocytes. (G) Immunofluorescence staining of the XY bodies in dispersed pachytene spermatocytes with an anti-SUMO-1 antibody. (H) Immunofluorescence staining of synaptonemal complexes (SC) in spermatocyte spreads with an anti-SCP3 antibody. Pachytene and diplotene spermatocytes were differentiated according to their SC structures. (I) Immunostaining of DAZAP1 on testis sections. The cell types are (P) pachytene and (Lp) leptotene spermatocytes. Scale bars, (C–E,J) 200 μm; (G) 10 μm; (I) 25 μm.