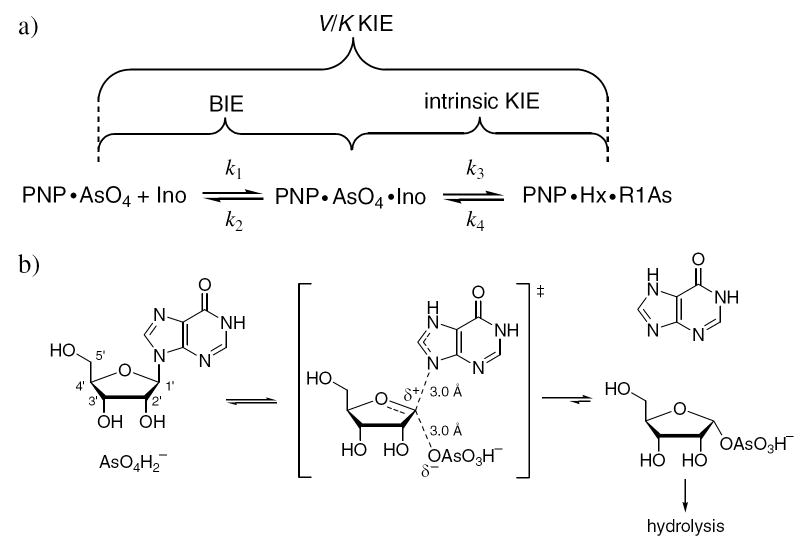
Figure 1.
a) The relationship among BIE, V/K KIE, and intrinsic KIE using purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) as a model. Ino = inosine, Hx = hypoxanthine, R1As = ribose 1-arsenate. b) Arsenolysis reaction catalyzed by purine nucleoside phosphorylase including the SN1-like transition state. Unlike the analogous phosphorolysis reaction, arsenolysis is irreversible due to the instability of the ribose 1-arsenate product, which rapidly hydrolyzes. N7 of the leaving group has been depicted as being protonated at the transition state, as this has been demonstrated to be a common mechanistic feature in PNP and other nucleoside phosphorylases and hydrolases (37).