Figure 3.
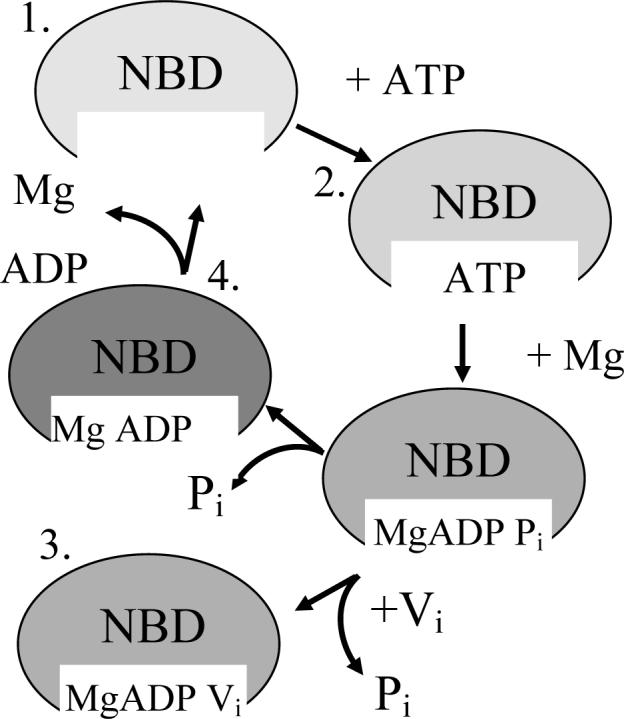
Cartoon of ATP binding and hydrolysis. The MsbA dimer contains two ATP binding sites that must interact to accomplish ATP hydrolysis. The four stages of ATP binding and hydrolysis have each been analyzed and are illustrated here. ATP binding is followed by the addition of MgCl2 immediately followed by sodium orthovanadate (Vi) to first allow hydrolysis of the γ-phosphate from ATP, leading to the ADP and Pi state, which is trapped and mimicked by the replacement of Pi with Vi. The final steps include the release of the Pi, leading to only ADP bound in the pocket, with its complete release reverting the enzyme back to the resting state.
