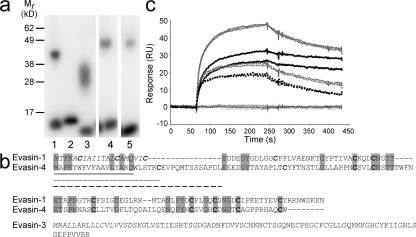
Figure 2.
Identification of Evasin-3 and -4. (a) Identification of Evasin-3 and -4 by cross-linking to radiolabeled chemokine in supernatants from transfected HEK293 cells. Viral CHBP p35 incubated with [125I]-CCL2 as a positive control in the presence (lane 1) or absence (lane 2) of the cross-linker BS3; supernatant from clone 69.19.1 incubated with [125I]-CXCL8 and BS3 (lane 3); supernatant from clone 10.27.1 incubated with [125I]-CCL5 and BS3 (lane 4) or [125I]-CCL11 and BS3 (lane 5). (b) Alignment of the predicted protein sequences of Evasin-1 and -4. Conserved residues are highlighted in gray and cysteines are shown in bold type. The predicted protein sequence of Evasin-3 is shown below the alignment. The signal peptides are shown in italics. Possible signal peptides of Evasin-4 are shown as follows: based on SignalJ prediction, black underline; based on secondary structure prediction, dotted underline; based on similarity to Evasin-1, dashed line. (c) Determination of the selectivity of immobilized recombinant Evasin-3 produced in E. coli by surface plasmon resonance. Sensograms corresponding to CXCL8 (bold black lines) CXCL1 (dotted black lines), MIP-2 (gray lines), and KC (dotted gray lines) showed strong binding of these chemokines to Evasin-3. The sensograms corresponding to CCL1, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL11, CCL18, CCL27, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL12, CXCL13, and CX3CL1 (black lines) indicated no binding of these chemokines to Evasin-3.