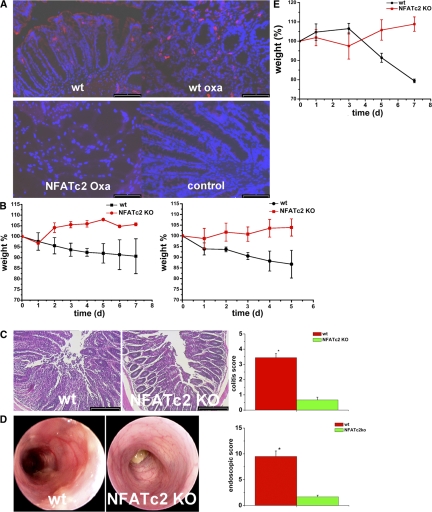
Figure 2.
A regulatory role of NFATc2 in oxazolone-induced experimental colitis. (A) Enhanced expression of the NFATc2 transcription factor in oxazolone-induced colitis. Colonic cryosections from WT and NFATc2 KO mice were incubated with anti-NFATc2 antibodies followed by tyramide signal amplification. An increased expression of NFATc2 was observed in colonic tissue from WT mice with oxazolone colitis (WT oxa) as compared with WT unchallenged mice. Colonic tissue from NFATc2 KO mice (NFATc2 oxa) served as negative control and did not reveal any specific staining as expected. (B) Oxazolone colitis was induced by sensitizing mice with oxazolone, followed by intrarectal administration of the hapten reagent after 1 wk. The body weight of the mice was monitored after oxazolone rechallenge at the indicated time points. Mean values ± the SEM from two representative experiments out of six are shown. The average weight of the mice at the beginning of the experiments was 22.9 g (WT group) and 22.5 g (NFATc2 KO group), respectively. For this experiment, 6 WT and 7 NFATc2 KO mice were used. (C) Histological sections (left) of colonic inflammation in WT or NFATc2-deficient mice upon oxazolone administration. Signs of inflammation such as goblet cell depletion, ulcers, and accumulation of mononuclear cells were noted in WT mice, whereas NFATc2 KO mice showed little or no evidence of colitis. Quantitative histopathologic assessment of colitis activity (right) showed a significant (*P < 0.05) protection from inflammation and tissue injury in NFATc2 KO mice compared with WT mice. Data represent mean values ± the SEM from one representative experiment out of six. (D) High-resolution miniendoscopic analysis (left) of the colon of NFATc2 KO and WT mice in oxazolone colitis. Marked erosions and ulcers were seen in the WT group, whereas an almost normal colon architecture was noted in NFATc2-deficient mice. Quantitative endoscopic analysis (right) of inflammation (MEICS score) in WT and NFATc2 KO mice in oxazolone colitis was done at day 2 after administration of oxazolone. A significantly (P < 0.05) lower endoscopic score was observed in NFATc2-deficient mice compared with WT mice. (E) Adoptive T cell transfer from WT and NFATc2-deficient mice in SCID mice. CD4+ T cells were transferred into CB-17/SCID mice, followed by oxazolone sensitization and intrarectal oxazolone administration. The body weight of reconstituted mice was analyzed at indicated time points. Mean values ± SEM from one representative experiment out of three are shown. Whereas mice reconstituted with WT T cells showed a marked weight loss, mice given NFATc2-deficient T cells were protected from colitis and gained weight. For this experiment five SCID mice in each group were used. Bars: (A) 80 μm; (C) 100 μm.