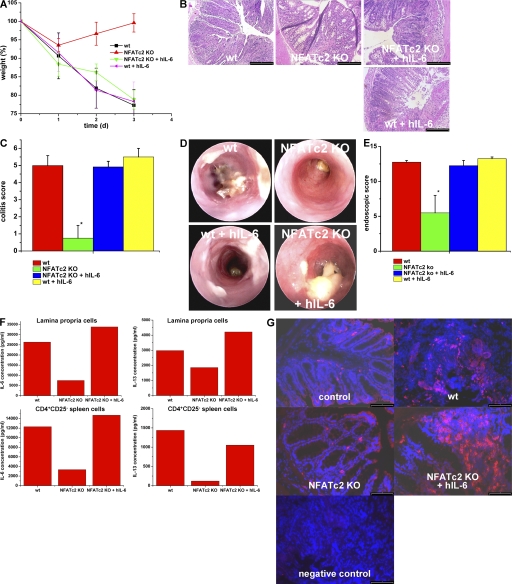
Figure 6.
Administration of hyper-IL-6 restores the susceptibility of NFATc2-deficient mice to oxazolone-induced colitis. (A) Oxazolone colitis was induced by sensitizing mice with oxazolone, followed by intrarectal administration after 7 d and monitoring of the body weight at indicated time points. Hyper IL-6 (hIL-6; 1 μg per mouse) was given i.p. before oxazolone administration. Weight curves from one representative experiment out of three are shown. Data represent mean values ± the SEM. Hyper-IL-6 administration led to colitis development and weight loss in oxazolone-treated NFATc2 KO mice, but had little effect on colitis activity in WT mice. This experiment was performed three times with groups of four to five mice. (B) Histological analysis of colonic inflammation in WT and NFATc2-deficient mice given PBS or hyper-IL-6. Signs of inflammation such as goblet cell depletion, erosions, and accumulation of mononuclear cells were noted in NFATc2-deficient mice treated with hyper-IL-6, but not control-treated NFATc2 KO mice. (C) Quantitative histopathologic assessment of colitis activity showed a significant (P < 0.05) protection from inflammation and tissue injury in NFATc2-deficient mice compared with WT mice, whereas no significant difference was noted between WT mice and NFATc2 KO mice given hyper-IL-6. Data represent mean values ± the SEM. (D) Endoscopic analysis of the colon of WT and NFATc2-deficient mice at day 2 after application of oxazolone. Oxazolone-induced erosions and ulcers were seen in the WT and NFATc2/hyper-IL-6 groups, whereas a normal colon architecture was noted in NFATc2-deficient mice. (E) Quantitative endoscopic score of inflammation (MEICS score). A significantly lower endoscopic score was observed in NFATc2-deficient mice compared with WT mice and NFATc2-deficient mice treated with hyper-IL-6. (F) IL-6 and -13 cytokine production by isolated CD4+CD25− splenic T cells and LPMCs in oxazolone colitis. Whereas NFATc2-deficient cells produced lower amounts of IL-6 and -13 than WT cells, hyper-IL-6 administration led to a strong induction of IL-6 and -13 production by cells lacking NFATc2. No changes in IFN-γ production were noted between NFATc2 KO mice and NFATc2 KO mice given hIL-6 (not depicted). (G) Increased numbers of CD4+ T cells in NFATc2-deficient mice after administration of hIL-6 in oxazolone colitis. Cryosections of colonic tissue were incubated with anti-CD4 antibodies and stained with conjugated Cy3 antibodies. An increased number of CD4+ T cells was observed in colonic tissue from WT mice during oxazolone-induced colitis compared with NFATc2 KO mice. After administration of hIL-6, NFATc2-deficient mice showed increased numbers of CD4+ T cells compared with NFATc2 mice without hIL-6 administration. Negative control staining is shown. Bars: (B) 100 μm; (G) 80 μm.