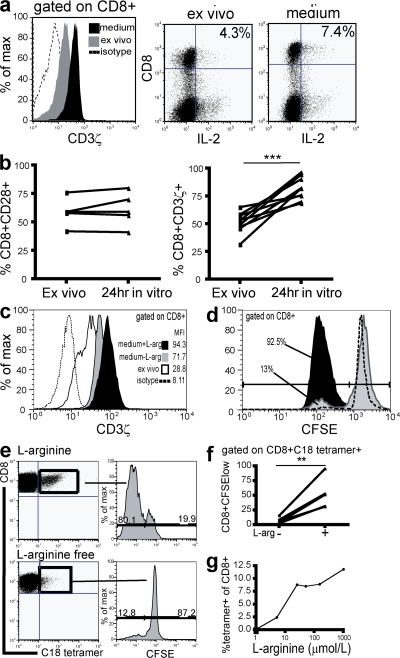
Figure 7.
Replenishment of arginine restores CD8 expression of CD3ζ, accompanied by a recovery in IL-2 production and proliferation. (a) Histogram illustrates effect of overnight culture in medium on CD3ζ levels (black histogram) compared with when measured directly ex vivo (gray histogram). Isotype control is shown as the dotted line. IL-2 production was determined in parallel before and after culture and representative plots are shown. (b) Cumulative data to show change in CD28 (P = nonsignificant) and CD3ζ expression (P < 0.0001) after in vitro culture, compared with ex vivo culture, in five and nine patients, respectively. (c) CD3ζ expression in CD8 T cells was determined directly ex vivo, and then again after overnight culture in medium with or without l-arginine (0.2 g/liter). (d) To investigate whether the presence of l-arginine affects CD8 T cell proliferation, PBMCs were preincubated with medium with or without l-arginine for 24 h, stained with CFSE, and resuspended in their respective mediums in the presence of a CD3ζ-dependent stimulus for 6 d. A gate has been applied on CD8 T cells. (e) To determine the effect of l-arginine on proliferation of HBV-specific CD8+ T cells, PBMCs from HLA-A2+ patients who had resolved HBV infection were stimulated with core 18–27 peptide for 7 d and detected with an HLA-A2/c18-27–specific tetramer. Representative dot plots depict the HBV-specific CD8+ population expanded at 1 wk, along with the number of divisions these populations have undergone, determined by CFSE dilution, in the presence (top) or absence (bottom) of l-arginine. (f) Cumulative data illustrate the effect of depleting l-arginine on the percentage of tetramer-positive populations dividing by 1 wk in 5 patients (P < 0.01). (g) HLA-A2/core18-27 tetramer-positive CD8 were compared after 7-d peptide stimulation of PBMCs incubated in a range of l-arginine concentrations (0 μM, 5 μM, 25 μM, 50 μM, 150 μM, and 1 mM).