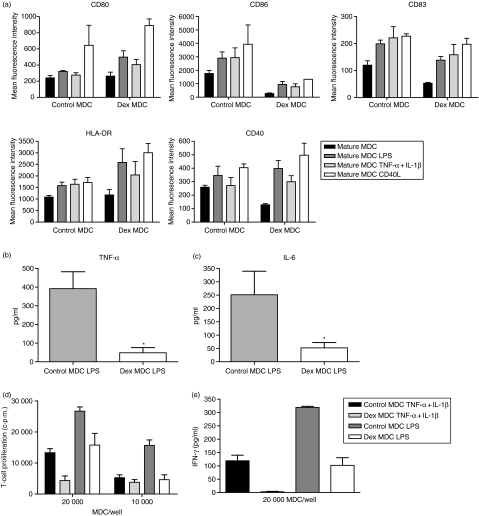
Figure 5.
Dex MDC are functionally resistant to a second maturation stimulus in the absence of dex. Control- and dex MDC were exposed to a second maturation stimulus in the absence of dex consisting of either LPS (100 pg/ml), TNF-α + IL-1β (50 pg/ml) or CD40L (5 × 103 000 J558 cells) for 24 hr. (a) The immunophenotypic characteristics of these MDC were determined by flow cytometry. Depicted is the mean fluorescence intensity of the various markers on control and dex MDC before (mature MDC) and after the second stimulus (mature MDC LPS, mature MDC TNF-α + IL-1β, mature MDC CD40L). Data represent mean with SEM of three separate experiments. (b) TNF-α levels in the culture supernatants of control and dex MDC 24 hr after restimulation with LPS. Data represent the mean with SEM of six separate experiments. *P = 0·03 for the comparison of dex MDC versus control MDC. (c) IL-6 levels in the culture supernatants of control or dex MDC 24 hr after restimulation with LPS. Data represent the mean with SEM of six separate experiments. *P = 0·03 for the comparison of dex MDC versus control MDC. (d) Allogeneic T-cell proliferation primed by control or dex MDC from the same donor that had been restimulated with LPS or TNF-α + IL-1β (one representative experiment out of three). (e) IFN-γ production in the supernatant on day 5 of the T cells stimulated by control or dex MDC that had been restimulated with LPS or TNF-α + IL-1β. Data represent mean with SEM of three separate experiments.