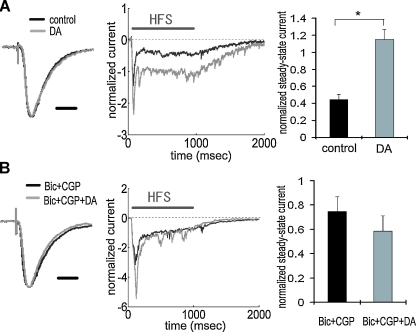
Figure 4.
Enhancement of TA-CA1 synaptic efficacy during HFS via DA-induced disinhibition. (A) Whole-cell voltage-clamp recording from CA1 pyramidal neurons. Waveforms represent the average of all data, showing normalized baseline EPSC (left) and current during HFS (middle). There was no difference in the kinetics of EPSC waveforms obtained with or without DA application. Waveforms during HFS (100 Hz 100 pulses) were normalized to baseline EPSC amplitude prior to HFS, and the current at the end of HFS (100th stimulus response) was measured (steady-state current). The right figure shows the analysis of steady-state current, showing that DA induced a significantly (p < 0.01) larger steady-state current. Input resistances were not significantly different (in MΩ; control: 85.8 ± 9.3, DA: 85.0 ± 9.0 (n = 6 for each group). Scale bar = 20 ms. (B) Same experimental procedure as A under GABA receptor blockade by bicuculline and CGP 55845A. GABA blockade attenuated the enhancement of steady-state current by DA. Input resistances were not significantly different (in M Ω; Bic + CGP: 102.0 ± 7.9, Bic + CGP + DA: 98.0 ± 4.6 (n = 5 for each group ). Scale bar = 20 ms.