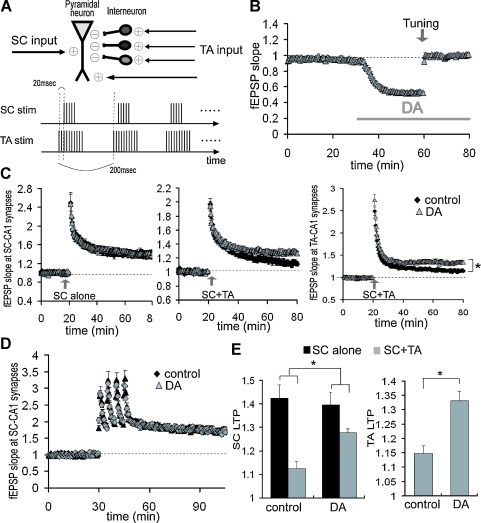
Figure 9.
Reduction of LTP interference at SC-CA1 synapses by DA-induced disinhibition at TA-CA1 synapses. (A) Scheme of LTP interference protocol. Bursts (10) of either 5 (SC) or 10 (TA) at 100 Hz with 200 ms interburst interval, was repeated twice at 30 second interval. TA-TBS precedes SC-TBS by 20 ms. (B) Compensation of DA-induced excitatory depression by increasing the stimulation current. After DA-induced depression was stabilized, the stimulation current was increased to return the fEPSP to its baseline value (tuning, indicated by arrow). (C) Influence of DA on the LTP interference of SC-CA1 synapses elicited by the TA pathway stimulation. TBS was applied to either the SC pathway alone (left; control: n = 8, DA: n = 6) or both the SC and the TA pathways concurrently (middle; n = 9 for each group). Right figure shows the enhancement of LTP at TA-CA1 synapses by DA after concurrent TBS application (n = 9 for each group). (D) No significant influence of DA on SC-LTP induced by HFS. LTP induction protocol was 100 Hz (100 pulse) stimulation, repeated 4 times at 5 minute intervals (n = 6 for each). (E) Analysis of DA's effects on the magnitude of LTP after TBS application, either at SC-CA1 synapses (left) or at TA-CA1 synapses. DA significantly attenuated the LTP interference at SC-CA1 synapses (p < 0.05), and enhanced LTP at TA-CA1 synapses (p < 0.01).