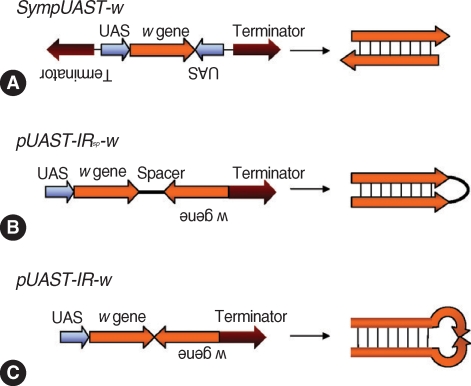
Fig. 3.
Strategies for generation of dsRNA in vivo by symmetric transcription. (A) SympUAST-w produces dsRNAs of the w gene by simultaneous transcription using two identical UAS promoters flanking the target gene in opposite directions. The target gene is transcribed in both directions and the resulting sense and antisense RNAs are hybridized to form dsRNAs. (B) pUAST-IRsp-w contains inverted repeats of the w gene with a spacer between the repeats. This is a common approach to generate hairpin dsRNAs. (C) pUAST-IR-w contains inverted repeats of the w gene without a spacer. This could generate hairpin dsRNAs, but the dsRNAs were not efficient enough to silence a target gene. This may be due to deletions in the center of inverted repeats, rendering the hairpin structure unstable. it appears that symmetrically transcribed dsRNA system may be effective enough to replace the inverted repeat hairpin RNAi system [113].