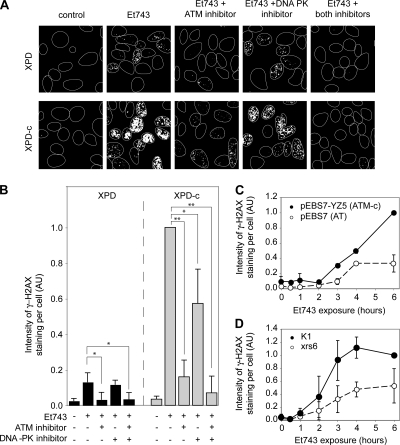
Figure 7.
Both ATM and DNA-PK phosphorylate H2AX in response to Et743 treatment. (A and B) Inhibition of Et743-induced formation of γ-H2AX foci by ATM- and DNA-PK-inhibitors (KU55933 and KU57788, respectively). XPD and XPD-c cells were preincubated with the ATM inhibitor (KU55933, 50 μM) and/or the DNA-PK inhibitor (KU57788, 20 μM) for 1 h before the addition of 10 nM Et743 for the next 6 h. (A) Representative pictures of γ-H2AX staining. (B) Quantification of the γ-H2AX staining intensity normalized to the number of cells analyzed (mean ± SD; n = 4; AU, arbitrary units; see Materials and Methods; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, Student's t test). (C) Reduced formation of γ-H2AX foci in the ATM-deficient cells (pEBS7) compared with their isogenic complemented counterparts (pEBS7-YZ5). Quantification of the intensity of the γ-H2AX staining normalized to the number of cells analyzed (mean ± SD, n = 3, AU, arbitrary units; see Materials and Methods). (D) Reduced γ-H2AX foci formation in DNA-PK–deficient xrs6 cells, compared with their wild-type counterpart (K1 cells). Quantification of the γ-H2AX staining intensity normalized to the number of analyzed cells (mean ± SD; n = 3; AU, arbitrary units; see Materials and Methods).