Figure 1.
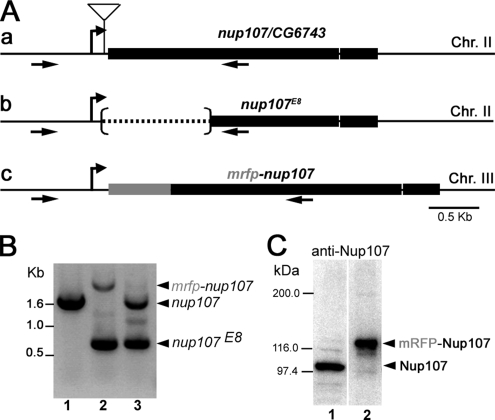
Structure of Drosophila nup107, mutants, and transgene. (A) a, schematic representation of the nup107 genomic locus on chromosome II. The thick line corresponds to the nup107 ORF, interrupted by a unique intron. The insertion site of the P element, located in the 5′UTR, 64 base pairs from the start codon of nup107 is indicated. b, imprecise excision of the P element generated the nup107E8 deletion allele lacking 976 nt from the translated region. c, the mRFP-nup107 transgene comprises ∼4.9 kb of the nup107 genomic locus and the mRFP ORF (inserted 18 base pairs upstream of the starting ATG of nup107). The transgene used in this study was integrated on chromosome III. Arrows indicate the position of the two primers used for the PCR in B. (B) PCR analysis of wild type (lane 1), the rescued line w−; nup107E8/nup107E8; P[mRFP-nup107] (lane 2), and nup107E8/+ heterozygotes (lane 3). (C) Total protein extracts of 0- to 3-h-old embryos from wild type (lane 1) and the mRFP-Nup107 rescued line flies (lane 2) were analyzed by Western blot using a polyclonal anti-Drosophila Nup107 antibody (see Materials and Methods). Endogenous Drosophila Nup107 (theoretical molecular mass of 97 kDa) is absent from the rescued flies (lane 2), in which mRFP-nup107 is the only source of Nup107. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the left. The original Western blot also including extracts from larvae and adult flies and the corresponding anti-tubulin staining of the membrane are provided in Supplemental Figure 1.