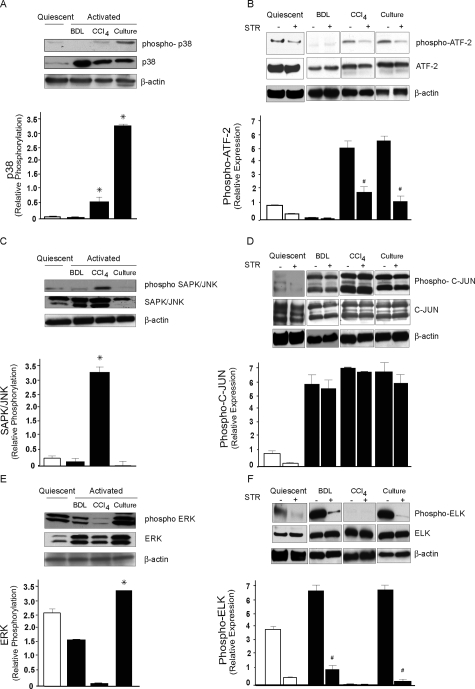
Figure 3.
MAPK expression and regulation by TGF-β in activated stellate cells in different liver injury models. Stellate cells were isolated from normal rat livers, BDL for 15 days and after four doses of CCl4 treatment as described in the Materials and Methods. A: Cell lysates (50 μg total protein) were subjected to immunoblotting using a specific phospho-p38 antibody. The membrane was stripped and reprobed with control p38 antibody. Data from different groups of cells were scanned, quantified, normalized, and presented graphically (n = 3, *P < 0.05 compared to quiescent stellate cells). B: Rats subjected to BDL- and CCl4-induced liver injury were exposed to STR as in the Materials and Methods or culture-activated stellate cells were incubated with STR as in Figure 1. Cellular proteins (200 μg of total protein) were used for immunoprecipitation with a specific threonine-tyrosine phospho-p38 MAP kinase antibody, followed by detection of phosphorylated p38 MAP kinase-specific substrate; ATF-2 by immunoblotting using phospho-ATF-2 antibody. As controls, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting using anti-ATF-2 antibody. Specific bands were scanned, quantified, normalized, and expressed graphically (n = 3, #P < 0.05 compared to controls without STR). C: Cell lysates (50 μg of total protein) were subjected to immunoblotting using a specific phospho-SAPK/JNK antibody. Membranes were stripped and reprobed with control SAPK/JNK antibody. For calculation of relative phosphorylation, bands corresponding to JNK 1 (46 kDa) were used and data from different group of cells were scanned, quantified, normalized, and presented graphically (n = 3, *P < 0.05 compared to quiescent stellate cells). D: Rats subjected to BDL- and CCl4-induced liver injury were exposed to STR as in the Materials and Methods or culture-activated stellate cells were incubated with STR as in Figure 1. An N-terminal C-JUN (1 to 89) fusion protein bound to glutathione Sepharose beads was used to selectively pull down SAPK/JNK from the cellular protein lysate (200 μg of total protein), followed by a kinase reaction. C-JUN phosphorylation was then measured by immunoblotting. As control, cellular proteins were immunoblotted with control C-JUN antibody. For relative quantification both bands for C-JUN phosphorylation (33 and 35 kDa) were used. E: Cell lysates (50 μg of total protein) were subjected to immunoblotting using a specific phospho-ERK antibody. Membranes were stripped and reprobed with control ERK antibody. For relative quantification both specific bands corresponding to phospho-ERK were used and data from different groups of cells were scanned, quantified, and presented graphically (n = 3, *P < 0.05 compared to quiescent stellate cells). F: Rats subjected to BDL- and CCl4-induced liver injury were exposed to STR as in the Materials and Methods or culture-activated stellate cells were incubated with STR as in Figure 1. Cellular proteins (200 μg of total protein) were used for immunoprecipitation with a specific monoclonal phospho-p44/42 antibody, followed by detection of phosphorylated p44/42 MAP kinase-specific substrate; ELK-1 by immunoblotting using phospho-ELK-1 antibody. As controls, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting using anti-ELK-1 antibody. Specific bands were scanned, quantified, normalized to the signal for β-actin, and presented graphically (n = 3, #P < 0.05 compared to controls without STR).