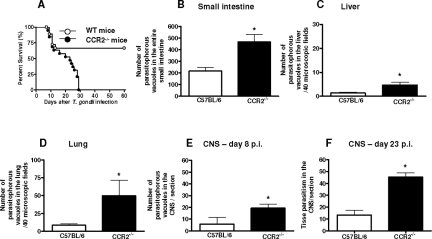
Figure 2.
Mortality rates and tissue parasitism of CCR2−/− and WT mice orally infected with five ME-49 T. gondii cysts. The mortality rate for eight mice from each group was determined (A). CCR2−/− mice were significantly more susceptible to toxoplasmosis than were WT mice (χ2 = 12.47; P = 0.0004; df = 1). The tissue parasitism in the small intestine (B), liver (C), lung (D), and CNS (E, F) were detected by immunohistochemistry staining and scored by counting the number of parasitophorous vacuoles per 40 microscopic fields in the peripheral organs and number of parasitophorous vacuoles and cyst-like structures per section in the CNS. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments of three mice per group that provided similar results (*P < 0.05).