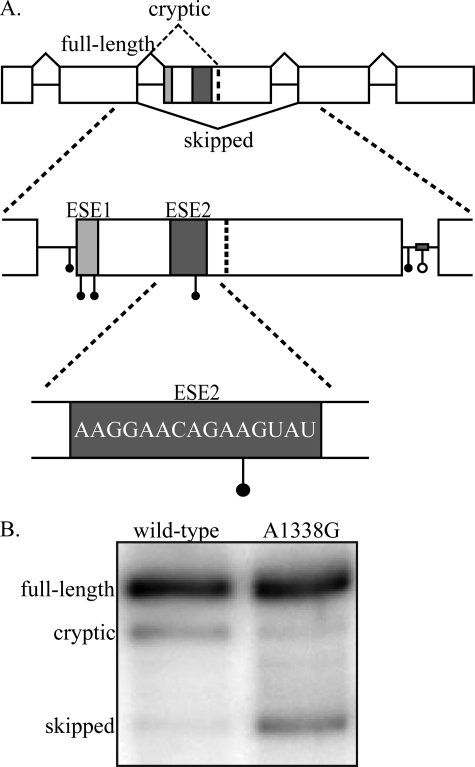
FIGURE 1.
GH1 gene structure and disease causing mutations. A, the GH1 gene is composed of five exons and four introns. Inclusion of all five exons (top, solid black lines) produces a mature transcript that encodes the 22-kDa, biologically active, full-length protein product. Splicing to a cryptic splice site in exon 3 (top, dashed black line) results in production of a 20-kDa, biologically active protein. Complete skipping of exon 3 (bottom, black line) produces a 17.5-kDa protein that acts as a dominant negative to the full-length, 22-kDa protein. Splicing of primary transcripts is regulated by two exonic splicing enhancers (ESE1, light gray box; ESE2, dark gray box) and one intronic splicing enhancer in intron 3 (gray bar). Point mutations (solid circles) and a deletion mutation (open circle) identified in patients suffering from isolated growth hormone deficiency type II fall into the following regions: intron 2 3′ splice site, exon 3 5′ splice site/ESE1, intron 3 5′ splice site, and intronic splicing enhancer. One patient mutation has been identified in ESE2 (E3+29 A→G; A1338G). The accession number for the complete sequence of GH1 is NM_000515.3. B, splicing analysis of wild-type and A1338G transcripts. GH3 rat somatotroph cells were transfected with either wild-type GH1 or GH1 containing the A1338G patient mutation. Total RNA was analyzed by RT-PCR, and the resulting products were separated on denaturing, polyacrylamide gels.