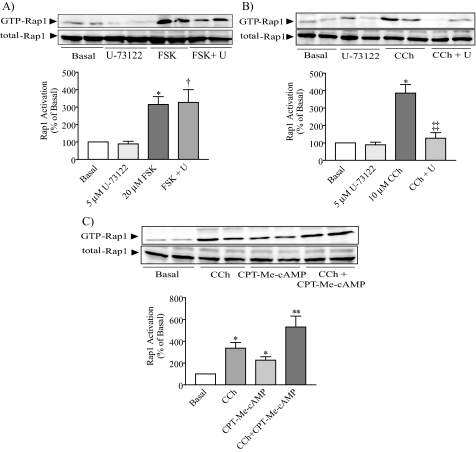
FIGURE 6.
The Epac1 pathway and the carbachol-induced pathway act independently to activate Rap1. Acini were pretreated with the PLC inhibitor U-73122 and then stimulated with either forskolin (A) or carbachol (B) for 10 min, and Rap1 activation was analyzed. The presence of the PLC inhibitor decreased carbachol-evoked GTP-Rap1 levels without affecting the response of forskolin. C, in other experiments, pancreatic acini were treated with either carbachol or 8-pCPT-2′-O-Me-cAMP (CPT-Me-cAMP) alone or with a combination of both for 10 min. The results showed that the co-addition of both stimulators induces an additive effect on Rap1 activation. The upper panels show representative immunoblots for GTP-Rap1 and total-Rap1. The lower panels show a quantitative analysis of Rap1 activation. Data shown are means ± S.E. (3–5 experiments) for Rap1 activation expressed as a percentage of basal. FSK, forskolin; CCh, carbachol. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus basal; †, p < 0.01 versus U-73122; ‡‡, p < 0.01 versus carbachol.