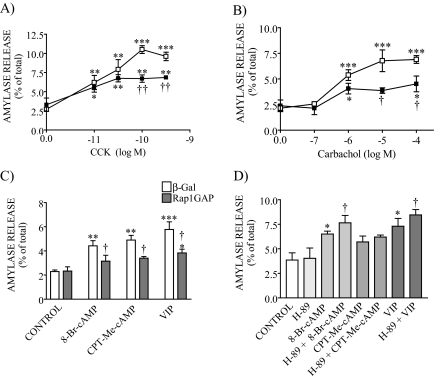
FIGURE 8.
GTP-Rap1 is involved in evoked pancreatic amylase release. β-Galactosidase (β-Gal; vector control) and Rap1GAP-overexpressing acini were stimulated with different concentrations of either CCK (A), carbachol (B), and cAMP-evoked secretagogues (C) for 30 min, and amylase release was measured. An inhibition of amylase secretion (40%) was observed when the Rap1GAP-overexpressing acini were stimulated with high concentrations of either CCK or carbachol. In addition, Rap1GAP overexpression decreased 8-Br-cAMP-, CPT-Me-cAMP-, and VIP-stimulated amylase secretion by 60%. Data shown are means ± S.E. (4–6 experiments) of amylase release expressed as a percentage of total. □, β-galactosidase-expressing cells; ▪, Rap1GAP-overexpressing cells. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 versus control; †, p < 0.05; ††, p < 0.01 versus CCK, carbachol, 8-Br-cAMP, CPT-Me-cAMP, or VIP response in β-galactosidase-expressing cells. D, pancreatic acini were preincubated for 10 min with the PKA inhibitor H-89 and then stimulated with 8-Br-cAMP, CPT-Me-cAMP, or VIP. Secretagogue-stimulated amylase release was not modified in the presence of the inhibitor. Data shown are means ± S.E. (four experiments) of amylase release expressed as a percentage of the total. *, p < 0.05 versus control; †, p < 0.05 versus 8-Br-cAMP or VIP.