FIGURE 3.
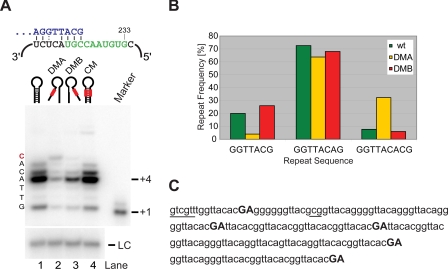
Boundary element disruption mutants result in extended reverse transcription products in vitro and in vivo. A, in vitro activity assay for wild type (lane 1), DMA (lane 2), DMB (lane 3), and CM (lane 4). Telomerase assays were carried out as described in Ref. 31. A 100-mer oligonucleotide was used as loading control (LC). A schematic for the alignment of the telomeric primer (blue) upstream of the template (green) is shown above the gel. Nucleotides added by telomerase are shown to the left of the gel. B, analysis of cloned telomere sequences from wild type (wt, n = 141), DMA (n = 83), and DMB (n = 79). Telomeres were isolated after 80 generations in the presence of the ter1 mutant, cloned by G overhang capture assay and sequenced. After trimming of the invariant proximal part of each telomere, the relative abundance of the three most common repeats was determined. C, sequences for the distal part of four telomeres isolated from DMA mutant cells. Read-through products are highlighted in bold, capital letters. Aberrant sequences found in only one telomere are underlined.