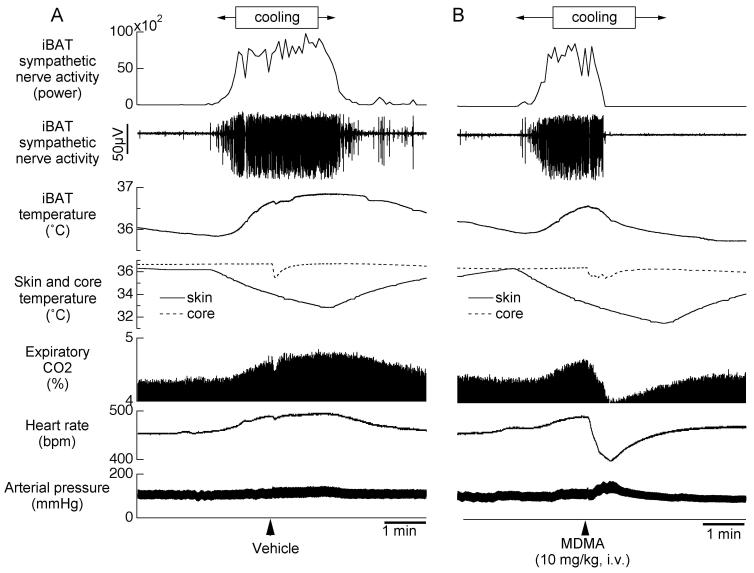
Fig 3.
Original records from different individual anesthetized rats showing the effect of Ringer vehicle (A) or MDMA (B) on directly recorded iBAT sympathetic nerve activity and other physiological parameters (see below) during a period when iBAT thermogenesis was increased by circulating cold water through a jacket around the rat’s body. From top panel to bottom panel; original recording of iBAT sympathetic nerve activity (SNA), iBAT SNA total power spectral density between 0 and 20Hz from autospectra of sequential 5.12-s segments of iBAT SNA, iBAT temperature, skin and core body temperature, expiratory CO2 concentration, heart rate (HR) and arterial pressure (AP). MDMA profoundly inhibits the cooling-induced increase in iBAT sympathetic nerve discharge, indicating an action within the CNS rather than in the periphery.