Figure 4. Chitin induces alternatively activated macrophages.
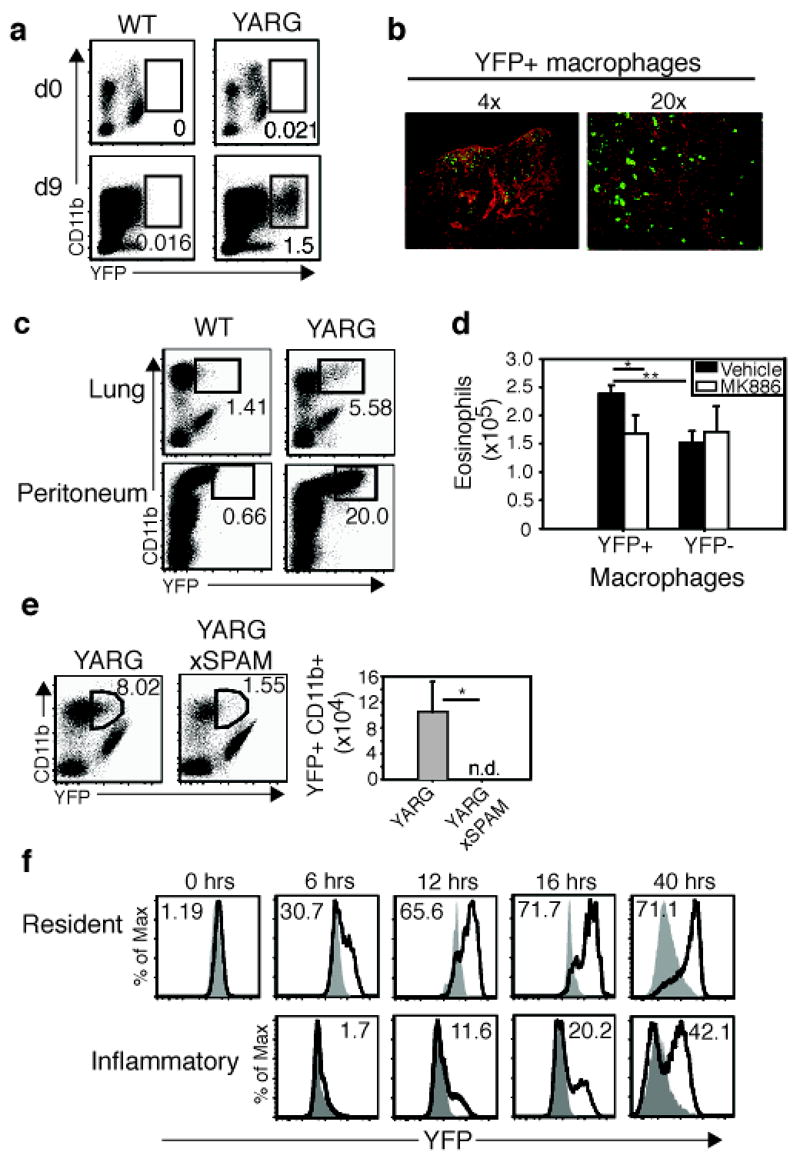
a, YARG or wild-type littermates were infected with N. brasiliensis. CD11b+ lung macrophages were analyzed for YFP expression on days 0 and 9. b, Day 9 N. brasiliensis-infected lung from YARG mice was stained with anti-GFP (green) and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (red). Lens magnification indicated. c, Chitin administered to lung or peritoneum of YARG or wild-type mice. d, Sorted YFP+ and YFP− macrophages were treated with vehicle or 10 μm MK886 for 10 min/37°C before analysis for eosinophil chemotaxis using a transwell assay. Results average of three independent experiments. e, YARGxSPAM transgenic mice were compared with YARG littermates following intranasal chitin. f, YARG mice or negative littermates received chitin and were analyzed for YFP expression. Filled histograms represent negative littermates. Solid line represents YFP in the YARG littermate. Numbers in the histogram are the percentage YFP+. Resident and inflammatory macrophages were subset using surface markers described in the text. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 P-values determined using Student’s t-test. Error bars represent standard deviations. In FACS plots, numbers represent percentage of gated cell from total live cells. n.d. = none detected. Each experiment represents two independent experiments with n=3 per group.
