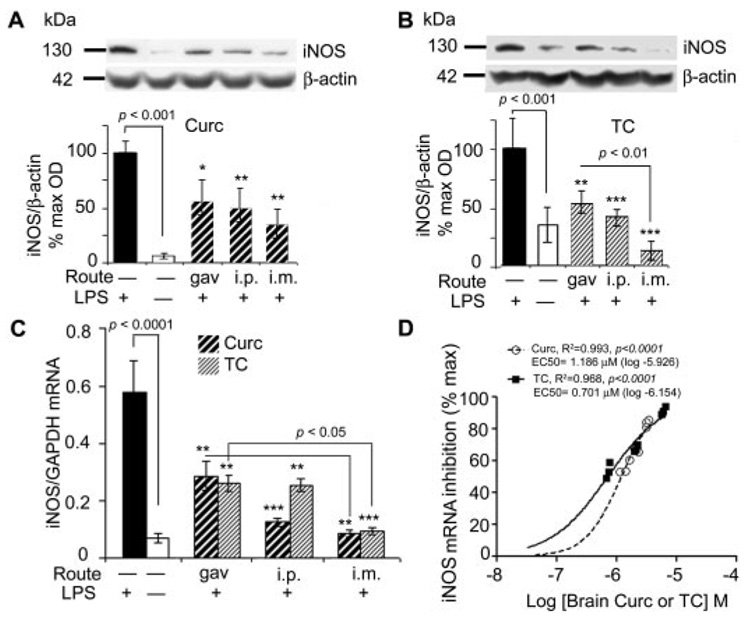
Fig. 3.
Curcumin and TC suppressed LPS-induced iNOS protein and mRNA. Mice injected with LPS or vehicle, were sacrificed 4 h after administration of curcumin (A) or TC (B), and the supernatant of TBS-extracted brains was electrophoresed on Western blot and immunostained with anti-iNOS and β-actin. Representative lanes and their densitometric quantitation are shown. C, RNA was extracted from brain and measured for iNOS mRNA using quantitative RT-PCR. D, percentage of iNOS inhibition was regressed on curcumin or TC concentrations. Closed circles, curcumin; open circles, TC. Values shown are the amount of iNOS mRNA as the mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.001 represent a significant difference compared with positive controls (LPS treatment alone; n = 4).