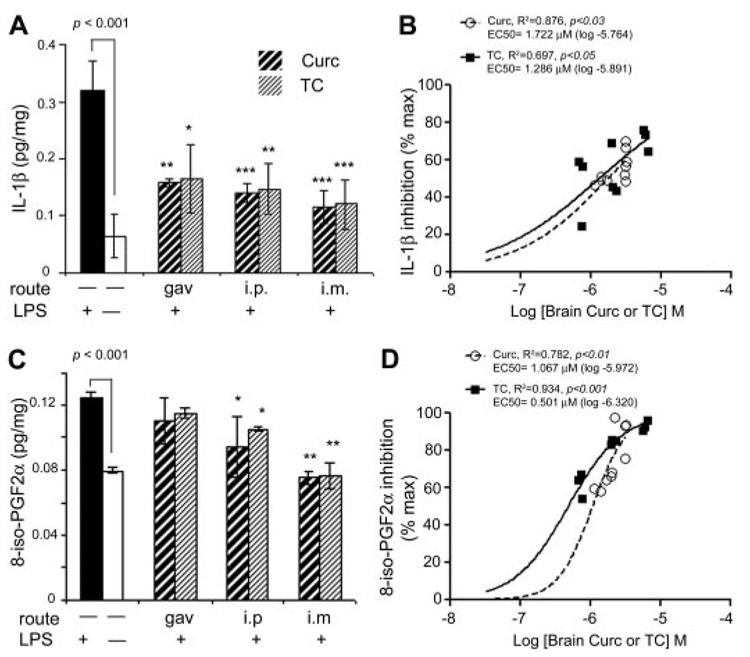
Fig. 4.
Acute injection of TC or curcumin similarly attenuated LPS induced-IL-1β or F2 isoprostane. A, quantitation of IL-1β levels in mouse brain homogenates was determined by sandwich ELISA. LPS injection (i.p.) increased IL-β levels more than 6-fold, an effect that was partially (>50%) suppressed by acute administration of either curcumin or TC, regardless of route of administration. B, either curcumin or TC levels correlated positively with percentage of IL-1β inhibition. C, lipid extracts of brain were measured for 8-iso-PGF2α by ELISA. The 40% increase in 8-iso-PGF2α caused by LPS was partially reduced by i.p. injection and completely suppressed by i.m injection of either compound. D, brain curcumin or TC correlated positively with brain F2 isoprostane inhibition. Values shown are the mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.001 represent significant difference compared with positive controls (LPS treatment alone; n = 4).