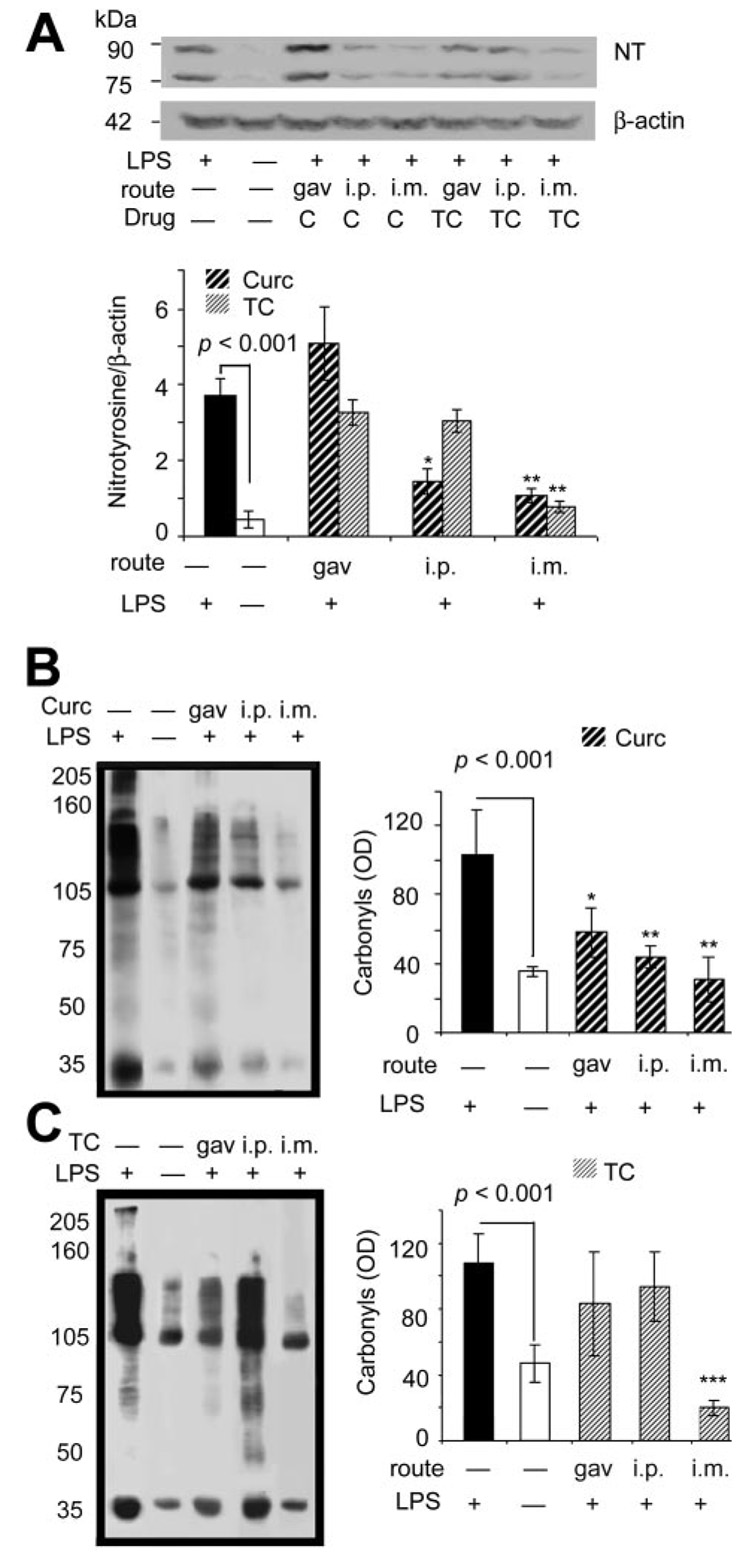
Fig. 5.
Acute curcumin or TC similarly suppresses LPS induction of brain NT, but curcumin is more effective at suppressing carbonyls. A, NT proteins increased more than 7-fold after LPS from mouse brain homogenates measured by Western blot with anti-nitrotyrosine antibody and normalized to β-actin. Injection (i.m.) of either compound suppressed NT induction. Injection (i.p.) of curcumin partially suppressed NT induction, whereas i.p. injection of TC did not affect NT induction. Oxidized protein levels of brain were determined in the lysis-extracted supernatant of the TBS-insoluble pellet using Oxyblot analysis with an anti-DNP antibody. Representative lanes are shown and quantified for curcumin- (B) or TC-(C) fed mice. Values shown are the mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 represent a significant difference compared with positive controls (LPS treated alone; n = 4).