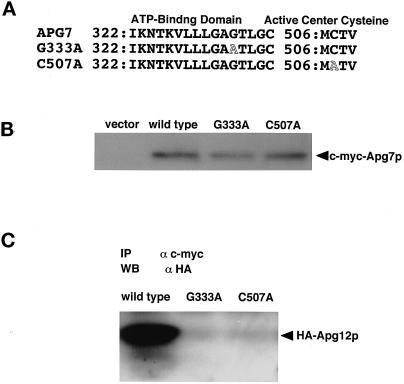
Figure 3.
The ATP-binding domain and active site cysteine of Apg7p are essential for conjugation with Apg12p via a thioester bond. (A) Point mutation sites are schematically represented. Gly333 in a predicted ATP-binding domain of Apg7p was changed to Ala by site-directed mutagenesis, and Cys507 in Apg7p was also changed to Ala. (B) Apg7pG333A and Apg7pC507A are expressed in yeast cells at similar levels to Apg7p. The apg7Δ strain carrying pRS314 (vector), strain YIT702 (wild type), strain YIT7G333A (G333A), and strain YIT7C507A (C507A) cells were grown in MVD medium and lysed. c-myc–tagged Apg7p proteins were immunoprecipitated as described in Figure 1A. (C) No Apg12p is coimmunoprecipitated with Apg7pG333A and Apg7pC507A. c-myc–tagged Apg7p in the cell lysate of YIT702 (wild type), YIT7G333A (G333A), and YIT7C507A (C507A) strains were immunoprecipitated, and the coimmunoprecipitates were detected by Western blotting with anti-HA antibody as described above.