Abstract
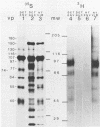
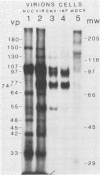
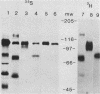
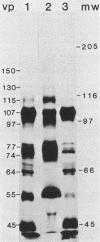
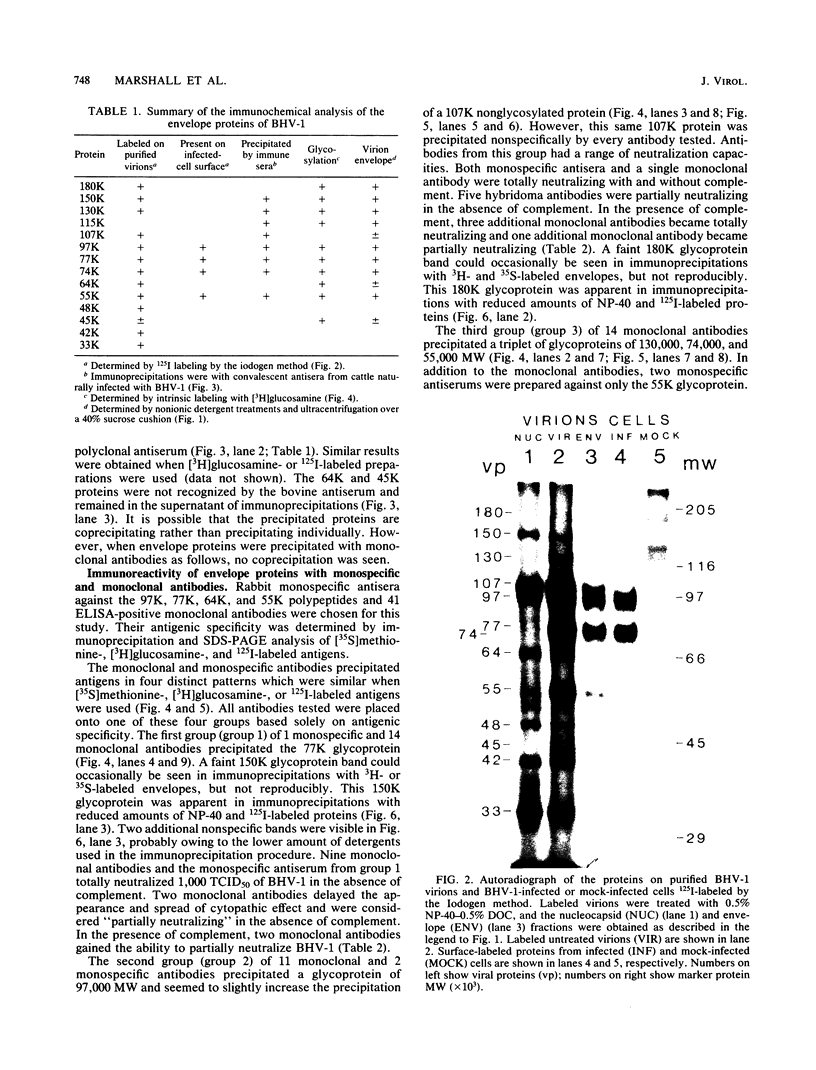
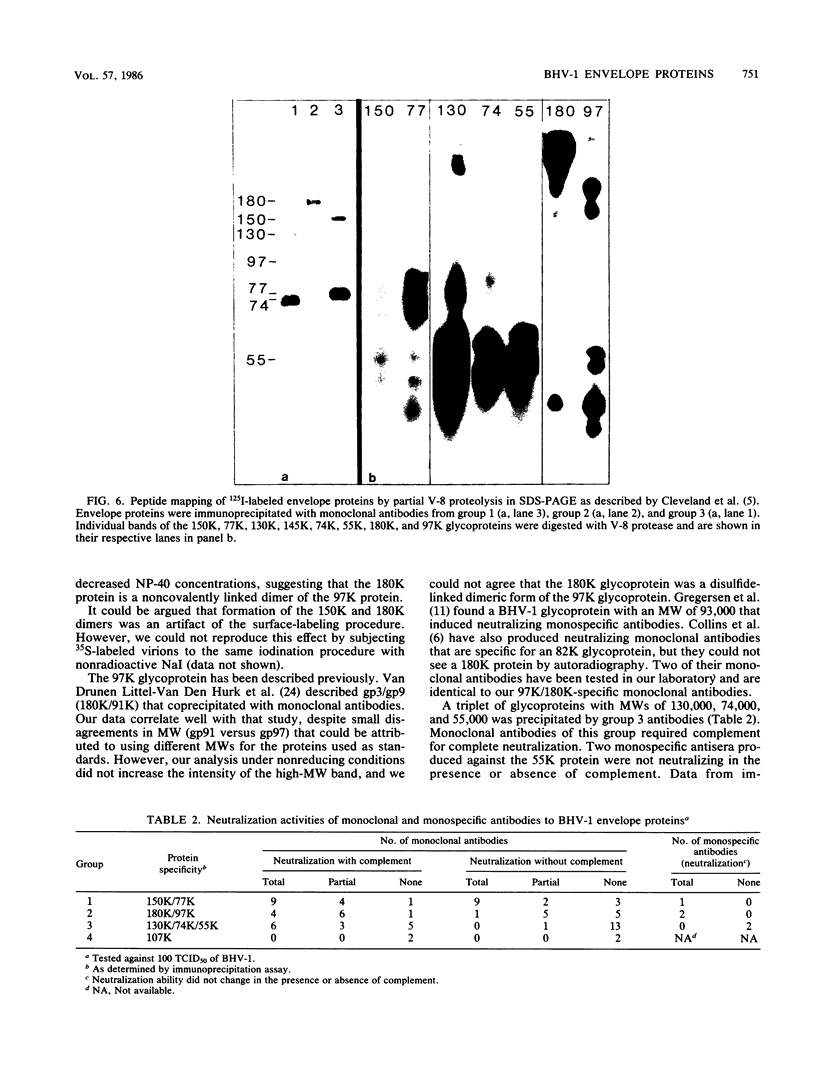
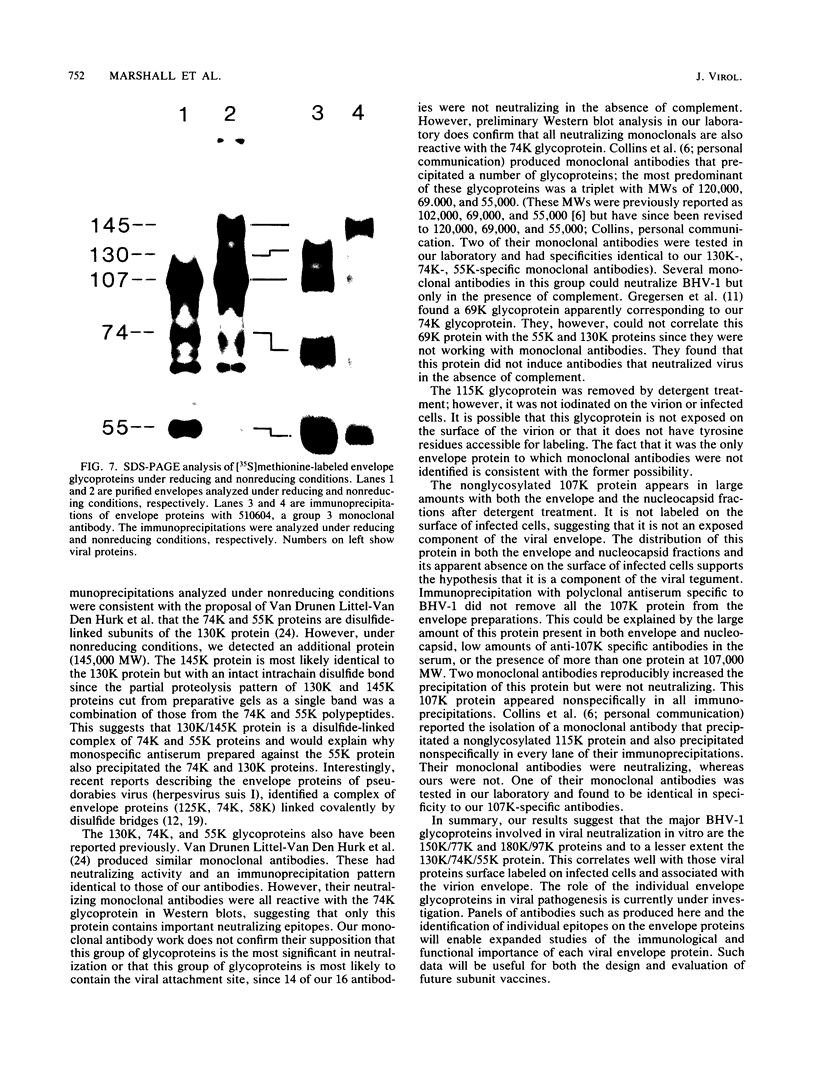
Ten glycoproteins of molecular weights of 180,000, 150,000, 130,000, 115,000, 97,000, 77,000, 74,000, 64,000, 55,000, and 45,000 (designated as 180K, 150K, etc.) and a single nonglycosylated 107,000-molecular-weight (107K) protein were quantitatively removed from purified bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) virions by detergent treatment. Immunoprecipitations with monospecific and monoclonal antibodies showed that three sets of coprecipitating glycoproteins, 180K/97K, 150K/77K, and 130K/74K/55K, were the major components of the BHV-1 envelope. These glycoproteins were present in the envelope of the virion and on the surface of BHV-1-infected cells and reacted with neutralizing monoclonal and monospecific antibodies. Antibodies to 150K/77K protein had the largest proportion of virus-neutralizing antibodies, followed by antibodies to 180K/97K protein. Monoclonal antibodies to 130K/74K/55K protein were neutralizing but only in the presence of complement; however, monospecific antisera produced with 55K protein did not have neutralizing activity. Analysis under nonreducing conditions showed that the 74K and 55K proteins interact through disulfide bonds to form the 130K molecule. Partial proteolysis studies showed that the 180K protein was a dimeric form of the 97K protein and that the 150K protein was a dimer of the 77K protein, but these dimers were not linked by disulfide bonds. The 107K protein was not glycosylated and induced antibodies that did not neutralize BHV-1. The 64K protein was not precipitated by anti-BHV-1 convalescent antisera, and monospecific antisera to this protein precipitated several polypeptides from uninfected cell lysates, suggesting that 64K is a protein of cellular origin associated with the BHV-1 virion envelope.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop G. A., Marlin S. D., Schwartz S. A., Glorioso J. C. Human natural killer cell recognition of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins: specificity analysis with the use of monoclonal antibodies and antigenic variants. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2206–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Zee Y. C., Ardans A. A. Identification of envelope and nucleocapsid proteins of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Feb;8(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter V. C., Schaffer P. A., Tevethia S. S. The involvement of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins in cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1655–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. K., Butcher A. C., Riegel C. A., McGrane V., Blair C. D., Teramoto Y. A., Winston S. Neutralizing determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies on polypeptides specified by bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):403–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.403-409.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J., Schröder C. H., Kumel G., Szczesiul M., Levine M. Immunogenicity of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gC and gB and their role in protective immunity. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):805–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.805-812.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen J. P., Pauli G., Ludwig H. Bovine herpesvirus 1: differentiation of IBR- and IPV-viruses and identification and functional role of their major immunogenic components. Arch Virol. 1985;84(1-2):91–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01310556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall C., Ionescu-Matiu I., Dreesman G. R. Utilization of the biotin/avidin system to amplify the sensitivity of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):329–339. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Mettenleiter T. C., Rziha H. J. Demonstration of three major species of pseudorabies virus glycoproteins and identification of a disulfide-linked glycoprotein complex. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):166–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.166-173.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupton H. W., Reed D. E. Evaluation of experimental subunit vaccines for infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Mar;41(3):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Blumenthal R. M., Babiuk L. A. Proteins Specified by bovine herpesvirus 1 (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus). J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):367–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.367-378.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Horohov D. W. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes in herpesvirus infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;6(1-2):35–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon S. K., Lawrence W. C., Long C. A., Rubin B. A., Sheffield J. B. Morphological components of herpesvirus. IV. Ultrastructural features of the envelope and tegument. J Ultrastruct Res. 1982 Nov;81(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(82)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Závada J., Huang A. S. Further characterization of proteins assembled by vesicular stomatitis virus from human tumor cells. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., van den Hurk J. V., Gilchrist J. E., Misra V., Babiuk L. A. Interactions of monoclonal antibodies and bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1) glycoproteins: characterization of their biochemical and immunological properties. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):466–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]