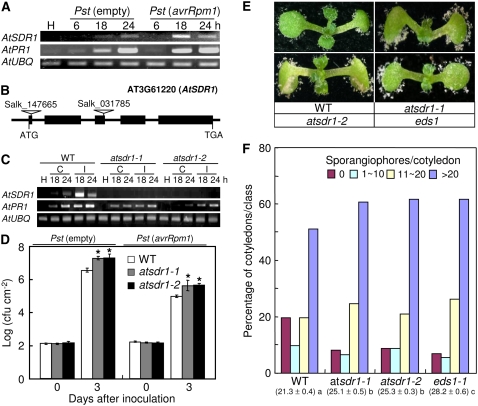
Figure 10.
Enhanced disease susceptibility of sdr1 Arabidopsis mutants. A, RT-PCR analyses of the expression of Arabidopsis AtSDR1 and AtPR1 in the leaves of wild-type Col-0 plants at 6, 18, and 24 h after inoculation with virulent (empty) and avirulent (avrRpm1) Pst DC30000. B, Schematic diagram showing AtSDR1 and its T-DNA insertion mutants. C, RT-PCR analyses of transcript levels of AtSDR1 and AtPR1 in leaf tissues of wild-type Col-0 and sdr1 mutant plants at 18 and 24 h after inoculation with virulent (compatible [C]) and avirulent (avrRpm1; incompatible [I]) Pst DC30000 (106 cfu mL−1). The AtSDR1 transcript is absent in sdr1 plants. D, Bacterial growth in the leaves of wild-type and sdr1 mutant plants at 0 and 3 d after inoculation with virulent (empty) and avirulent (avrRpm1) strains of Pst DC3000 (5 × 104 cfu mL−1). Asterisks indicate significant differences as determined by Student's t test (P < 0.05). E, Disease symptoms on the cotyledons of wild-type and sdr1 mutant plants at 7 d after inoculation with H. parasitica (5 × 104 spores mL−1). F, Numbers of sporangiophores per cotyledon of wild-type and sdr1 mutant plants at 7 d after inoculation with H. parasitica. Diseased cotyledons were classified as follows: no sporulation (no sporangiophores per cotyledon), light sporulation (approximately 1–10 sporangiopores per cotyledon), medium sporulation (approximately 11–20 sporangiophores per cotyledon), or heavy sporulation (more than 20 sporangiophores per cotyledon). Sporangiophores were counted on more than 50 cotyledons per genotype. Average numbers of sporangiophores on the cotyledons of wild-type and mutant lines are shown at bottom for each of the lines tested. Statistically significant differences between means were determined employing the lsd (P = 0.05).