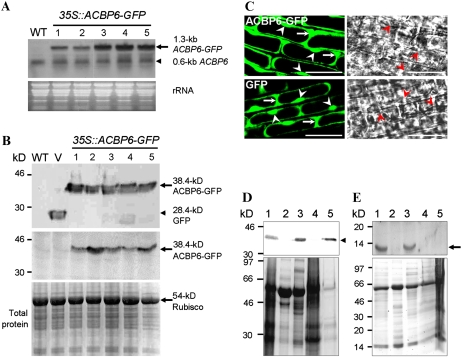
Figure 1.
Subcellular localization of ACBP6 in Arabidopsis. A, Northern-blot analysis with digoxigenin-labeled ACBP6 cDNA of five independent 35S∷ACBP6-GFP transgenic lines (lanes 1–5). The arrow indicates ACBP6-GFP mRNA, and the arrowhead indicates ACBP6 mRNA. An RNA gel (30 μg lane−1) stained with ethidium bromide is shown at bottom. WT, Wild type. B, Western-blot analyses using anti-GFP (top) and ACBP6-specific (bottom) antibodies on the same five independent 35S∷ACBP6-GFP transformants. ACBP6-GFP (arrows) and GFP (arrowhead) cross-reacting bands are indicated. The bottom panel shows a gel identically loaded and stained with Coomassie Blue. V, Vector-transformed control. C, Confocal microscopy of premature root cells of Arabidopsis 35S∷ACBP6-GFP line 1 (top) showing the localization of ACBP6-GFP in the cytosol (arrows) and nuclei (arrowheads). GFP vector-transformed Arabidopsis is shown at bottom. Bars = 20 μm. D, Western-blot analysis using anti-GFP antibodies on subcellular fractions of whole plant protein from transgenic Arabidopsis 35S∷ACBP6-GFP line 1. Subcellular fractions are from total whole plant protein (lane 1), membrane (lane 2), cytosol (lane 3), large particles including mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes (lane 4), and nuclei (lane 5). The arrowhead indicates a 38.4-kD ACBP6-GFP cross-reacting band. The bottom panel shows a gel identically loaded and stained with Coomassie Blue. E, Western-blot analysis using ACBP6-specific antibodies on subcellular fractions of whole plant protein from wild-type Arabidopsis. Subcellular fractions are from total whole plant protein (lane 1), membrane (lane 2), cytosol (lane 3), large particles including mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes (lane 4), and nuclei (lane 5). The arrow indicates a 10.4-kD ACBP6 cross-reacting band. The bottom panel shows a gel identically loaded and stained with Coomassie Blue.