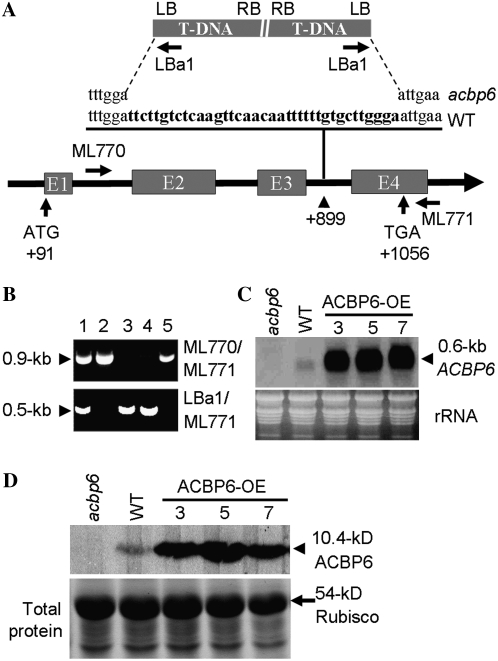
Figure 3.
Characterization of the acbp6 knockout mutant (SALK_104339) and 35S∷ACBP6 transgenic Arabidopsis. A, T-DNA insertion in the third intron of ACBP6 resulted in a 37-bp deletion (boldface in the wild-type [WT] sequence). The locations of primers used to genotype the acbp6 allele are shown. B, Specificity of the primer combinations ML770/ML771 (top gel) and LBa1/ML771 (bottom gel) in PCR to identify acbp6 homozygous mutants (lanes 3 and 4). The samples in lanes 2 and 5 resemble wild-type samples. Lane 1, Heterozygous mutant. C, Northern-blot analysis of wild type, acbp6 mutant, and ACBP6 overexpressor (OE-3, OE-5, and OE-7) plants using a digoxigenin-labeled ACBP6 cDNA probe. The acbp6 homozygous mutant lacked ACBP6 mRNA. ACBP6 overexpressor lines showed higher ACBP6 expression than the wild type. Total RNA (30 μg lane−1) stained with ethidium bromide before blotting is shown at bottom. D, Western-blot analysis using ACBP6-specific antibodies. Total protein (15 μg lane−1) was extracted from rosettes of wild-type, acbp6 mutant, and three independent ACBP6 overexpressor (OE-3, OE-5, and OE-7) plants. The bottom panel shows a gel identically loaded and stained with Coomassie Blue.