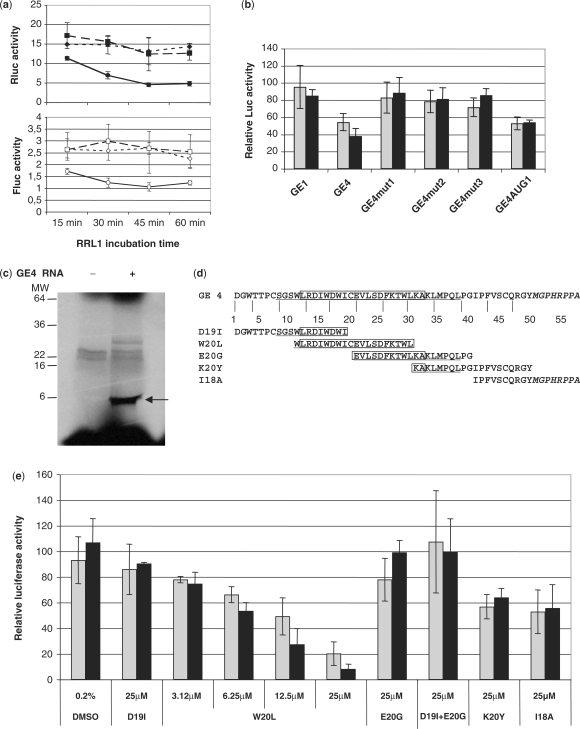
Figure 3.
Analysis of GE4 mechanism of action on translation. (a) Result of a typical two-step translation assay using RNA encoding GE1(squares), GE4 (circles) or no RNA (diamonds), incubated in RRL1 for the indicated period of time: cap-dependent Fluc (open symbols, lower figure) and HCV IRES-dependent Rluc (closed symbols, upper figure) activities in RLL2 are expressed as absolute RLU (× 106) values per assay (mean ± SEM of triplicate). (b) Effect of mutations in GE4 RNA on cap-dependent Fluc (light bars) and HCV IRES-dependent Rluc (dark bars) activities. GE4 RNA, either wild-type (GE4) or mutated at the level of the first AUG (mut1), the 1st and the 2nd AUGs (mut2), the 3AUGs (mut3) or the 2nd and 3rd AUGs (AUG1), was translated in RRL1 as in Figure 3a. The results are expressed as the percentage of RRL2 luciferase activity without RNA, obtained with a 45-min RRL1 (mean ± SEM of at least four experiments). (c) SDS–PAGE of the translation product of GE4 RNA (right lane), indicated by an arrow. GE4 RNA has been translated for 45 min in RRL1 mix, in the presence of S35-methionine, as recommended by the manufacturer. In the left lane, no RNA has been added. (d) Amino acid sequence of GE4 and GE4-derived synthetic peptides. The NS5A N-terminal membrane anchor domain is underlined. The amino acids L12–A32 form an amphipatic α-helix (boxed). (e) The synthetic peptides and the W20L solvent (0.2% DMSO) were tested for their effect on pIRF-3′NC RNA translation in the RRL2 translation assay. The luciferase activities are expressed as the percentage of activity in the absence of peptide (mean ± SEM of three independent experiments).