Abstract
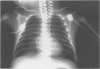
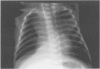
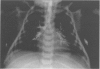
Between 1988 and 1992, 18 mechanically ventilated newborn babies (mean weight 1300 g and gestational age 30 weeks) presented with deteriorating respiratory failure at a mean age of 29 days. All developed increased oxygen requirements, hypoxic and hypercapnic episodes, and radiological changes of fixed lobar emphysema or recurrent atelectasis which sometimes changed sides from one day to another. Tracheobronchography with iopydol-iopydone was normal in five (27%) cases, but in 13 showed tracheobronchial stenosis localised to the lower trachea (seven cases), to the right main bronchus (three cases), or including the left main bronchus (four cases). Eleven of these 13 patients underwent endoscopy and balloon dilatation of the stenotic area. Five patients died, one before endoscopy, one immediately after endoscopies, and three subsequently with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The other six babies recovered without any sequelae after balloon dilatation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey C., Kattwinkel J., Teja K., Buckley T. Shallow versus deep endotracheal suctioning in young rabbits: pathologic effects on the tracheobronchial wall. Pediatrics. 1988 Nov;82(5):746–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B., Hedlund G. L., Glasier C. M., Williams K. D., Greenwood L. H., Gilliland J. D. Tracheobronchial stenosis in infants: successful balloon dilation therapy. Radiology. 1987 Aug;164(2):475–478. doi: 10.1148/radiology.164.2.3602388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. D., Weber T. R., Rao C. C. Balloon dilatation of tracheal and bronchial stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Mar;142(3):477–478. doi: 10.2214/ajr.142.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dab I., Malfroot A., Goossens A. Therapeutic bronchoscopy in ventilated neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Nov;69(5 Spec No):533–537. doi: 10.1136/adc.69.5_spec_no.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankle S. K., Schuller D. E., McClead R. E. Risk factors for neonatal acquired subglottic stenosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1986 Nov-Dec;95(6 Pt 1):626–630. doi: 10.1177/000348948609500617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlieger H., Wilms G., Marchal G., Jaeken J., Baert A., Eggermont E. Sténoses trachéo-bronchiques du nouveau-né prématuré. Traitement par dilatation au ballonnet. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1988 Oct;45(8):561–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkerbout S. C., van Lingen R. A., Gerritsen J., Roorda R. J. Endoscopic balloon dilatation of acquired airway stenosis in newborn infants: a promising treatment. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Jan;68(1 Spec No):37–40. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.1_spec_no.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg J., Forte V. Acquired bronchial injury in neonates. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1987 Dec;14(2-3):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0165-5876(87)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenholz S. K., Hall R. J., Lilly J. R., Shikes R. H. Surgical implications of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr Surg. 1987 Dec;22(12):1132–1136. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(87)80723-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groff D. B., Allen J. K. Gruentzig balloon catheter dilation for acquired bronchial stenosis in an infant. Ann Thorac Surg. 1985 Apr;39(4):379–381. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62638-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grylack L. J., Anderson K. D. Diagnosis and treatment of traumatic granuloma in tracheobronchial tree of newborn with history of chronic intubation. J Pediatr Surg. 1984 Apr;19(2):200–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(84)80451-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauft S. M., Perlman J. M., Siegel M. J., Muntz H. R. Tracheal stenosis in the sick premature infant. Clinical and radiologic features. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Feb;142(2):206–209. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150020108042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennequin Y., Pardou A., Detemmerman D., Vermeylen D., Muller F., Vandermoten G., Avni E. F. Partial bronchial stenosis following inadvertent right bronchial intubation in a neonate. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 1985 Sep;36(3):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. M., O'Brodovich H. Airway epithelial damage in premature infants with respiratory failure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):450–457. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir P., Bougatef A., Ramet J., Dab I., Cham B., Sacré L. Nonsurgical intervention in the resolution of acquired neonatal bronchial stenosis. Am J Perinatol. 1990 Jul;7(3):290–292. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-999505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl H., Rintala R., Malinen L., Leijala M., Sairanen H. Bronchoscopy during the first month of life. J Pediatr Surg. 1992 May;27(5):548–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(92)90442-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. W., Woo P., Kellman R. K., Slagle T. S. Tracheobronchial abnormalities in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1987 Nov;111(5):779–782. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraj H. S., Shott R., Fellows R., Yacoub U. Recurrent lobar atelectasis due to acquired bronchial stenosis in neonates. J Pediatr Surg. 1980 Aug;15(4):411–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(80)80745-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northway W. H., Jr, Rosan R. C., Porter D. Y. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 16;276(7):357–368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702162760701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippart A. I., Long J. A., Greenholz S. K. Balloon dilatation of postoperative tracheal stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 1988 Dec;23(12):1178–1179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(88)80337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roopchand R., Roopnarinesingh S., Ramsewak S. Instability of the tracheal tube in neonates. A postmortem study. Anaesthesia. 1989 Feb;44(2):107–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1989.tb11156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. M., Nelson H. Decreased incidence of subglottic stenosis using an "appropriate-sized" endotracheal tube in neonates. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1989;6(3):183–185. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950060311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinwell E. S. Ultrathin fiberoptic bronchoscopy for airway toilet in neonatal pulmonary atelectasis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1992 May;13(1):48–49. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950130112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire R., Brodsky L., Rossman J. The role of infection in the pathogenesis of acquired tracheal stenosis. Laryngoscope. 1990 Jul;100(7):765–770. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199007000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D. A., John E., Osborn R. A. Epithelial damage beyond the tip of the endotracheal tube. Early Hum Dev. 1990 Dec;24(3):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(90)90026-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]