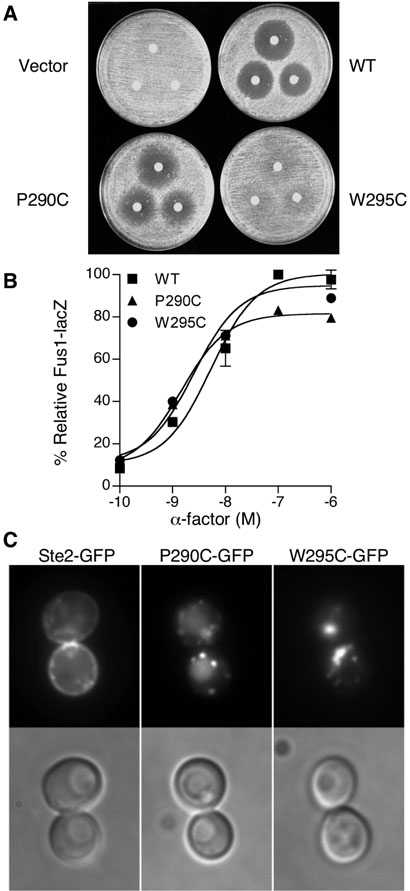
Figure 2.
Analysis of the effects of the P290C and W295C substitutions on Ste2 function and plasma membrane localization. (A) Halo assays for cell division arrest. Filter disks containing a-factor (375, 750, or 1500 ng) were applied onto agar plates spread with a lawn of yeast carrying the empty vector or indicated STE2 plasmid. Cell division arrest results in formation of zone of growth inhibition (halo) surrounding the filter disk. (B) Dose response assays for the pheromone-responsive Fus1-lacZ reporter gene. Cells carrying the indicated wild-type or mutant versions of STE2 on a plasmid were assayed for induction of the FUS1-lacZ reporter gene in response to a-factor. The β-galactosidase values were normalized to the maximal value of wildtype cells. The results represent the average of three independent experiments, each done in triplicate. (C) Fluorescence microscope images of the cellular localization of wild type, P290C and W295C versions of Ste2-GFP. Experiments were carried out with ste2Δ strain yLG123.