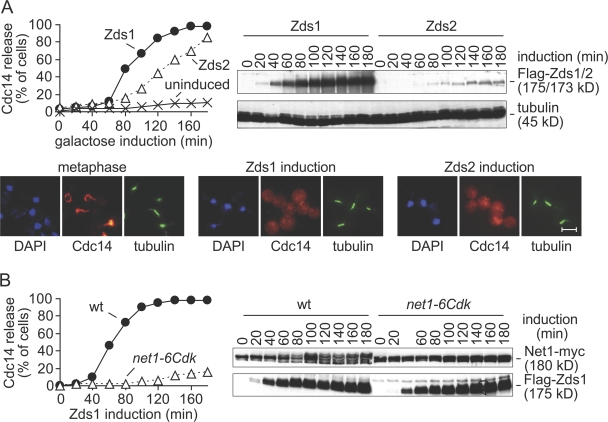
Figure 3.
Zds1 promotes Cdc14 nucleolar release by Net1 phosphorylation. (A) Ectopic expression of Zds1 and Zds2 promote Cdc14 nucleolar release. Strains Y3288 (MATa MET-CDC20 GAL-Flag-ZDS1 CDC14-Pk9) and Y2220 (MATa MET-CDC20 GAL-Flag-ZDS2 CDC14-Pk9) were arrested in metaphase (meta) and Zds1 or Zds2 expression induced. Part of the culture of strain Y3288 was maintained without Zds1 induction during the course of the experiment. Cdc14 nucleolar release was monitored by immunofluorescence, and Zds1 and Zds2 expression levels were analyzed by Western blotting. Tubulin served as a loading control. Photographs are shown of cells in metaphase and 120 min after Zds1 or Zds2 induction. Bar, 5 μm. (B) Cdk phosphorylation sites are required for Zds1-induced Net1 phosphorylation and Cdc14 release. Strains Y1008 (MATa MET-CDC20 GAL-Flag-ZDS1 CDC14-Pk9 NET1-myc9) and Y1013 (as Y1008, but net1-6Cdk-myc9) were arrested in metaphase by Cdc20 depletion and Zds1 expression was induced. Net1 phosphorylation was monitored by Western blotting against the myc epitope. Apparent relative molecular weights are indicated.