Figure 4. Location of isoform specific amino acid residues in the myosin molecule.
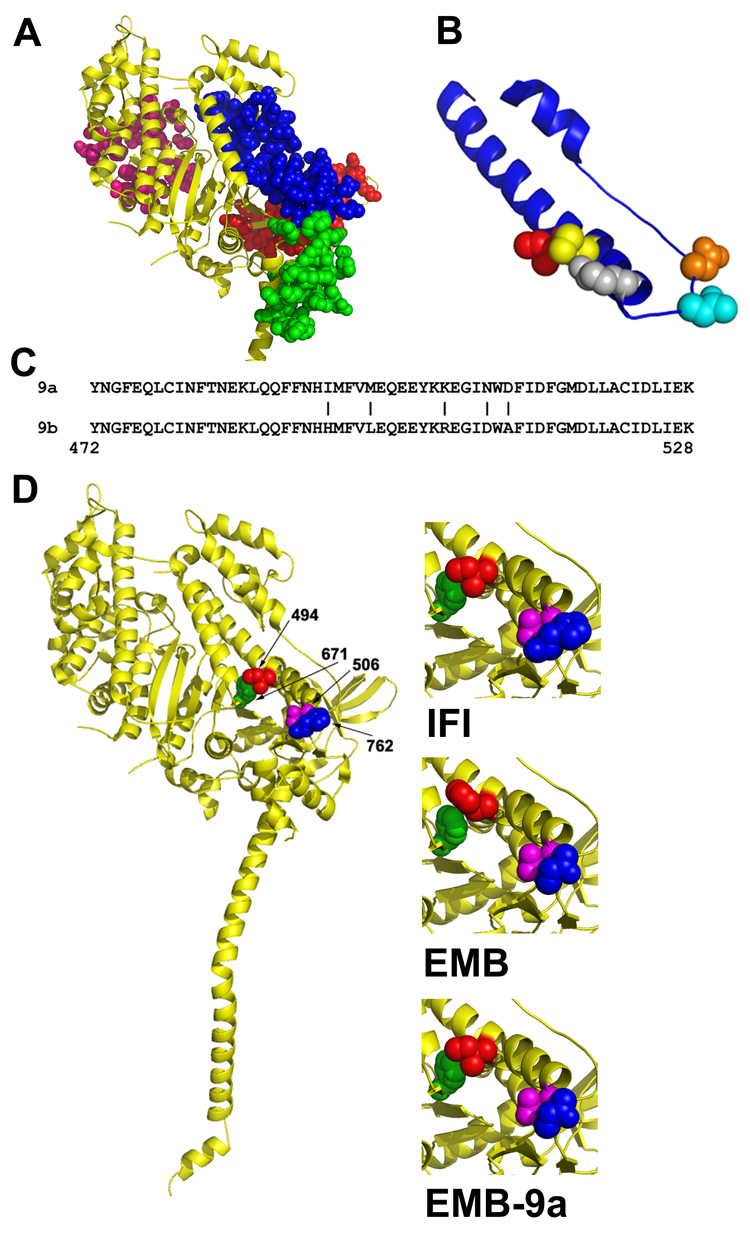
A, Location of the domains encoded by alternative exons in Drosophila MHC. Exon 3 (red), exon 7 (pink), exon 9 (blue) and exon 11 (green) domains are mapped onto the crystal structure of scallop myosin S-1 in the pre-power stroke state.31 The only interactions observable between the relay domain (encoded by exon 9) and other alternative domains are with the converter domain (encoded by exon 11). B, Close-up view of the relay domain (blue) encoded by Drosophila alternative exon 9. The five IFI-specific amino acids encoded by exon 9a are mapped on the molecule as red (Ile-494), yellow (Met-498), grey (Lys-505), cyan (Asn-509) and orange (Asp-511). C, The amino acid sequence of the two alternative relay domains; a vertical line (|) marks each of the five amino acid differences encoded by exon 9a and exon 9b. The chicken pectoralis muscle myosin numbering system is used. D, Mapping of Drosophila amino acids onto the crystal structure of scallop myosin S-1 in the pre-power stroke state.31 Interacting amino acids in IFI (left and upper right) are Ile-494 (red) with Phe-671 (green) and Glu-506 (magenta) with His-762 (blue). The same color scheme is used to map the corresponding amino acids in EMB (middle right; His-494, Phe-671, Glu-506, Asn-762) and in the chimeric EMB-9a myosin (lower right; Ile-494, Phe-671, Glu-506, Asn-762).
