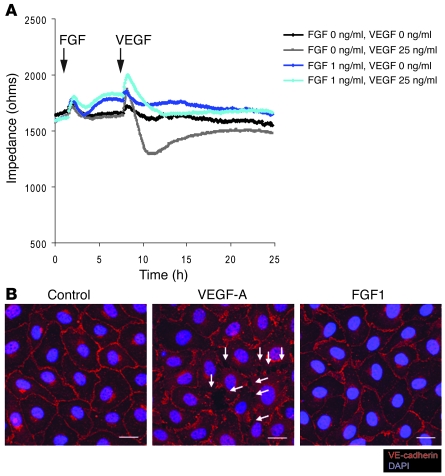
Figure 8. FGF treatment maintains EC junctions and decreases endothelial permeability in vitro.
(A) ECIS permeability assay using confluent monolayer. BAECs are matured to full confluency and the medium was replaced to 1% BSA in EBM-2 (Cambrex). FGF1 (1 ng/ml) or 1% BSA/EBM-2 was added at the indicated time point (arrow). Six hours later, VEGF-A (25 ng/ml) or 1% BSA/EBM2 was added at the indicated time point (arrow). At 6 hours, FGF treatment significantly increased monolayer impedance compared with the control treatment. (B) FGF treatment does not induce junction disruption on endothelial cell monolayers. BAECs are matured to full confluency, starved with 1% BSA in EBM-2 for 48 hours, and treated with either FGF1 (50 ng/ml) or VEGF (80 ng/ml) for 30 minutes Note with this condition, VEGF rapidly disrupts endothelial cell junctions (white arrows) whereas FGF treatment maintains junctions similar to those in the control monolayer. Scale bars: 20 μm.