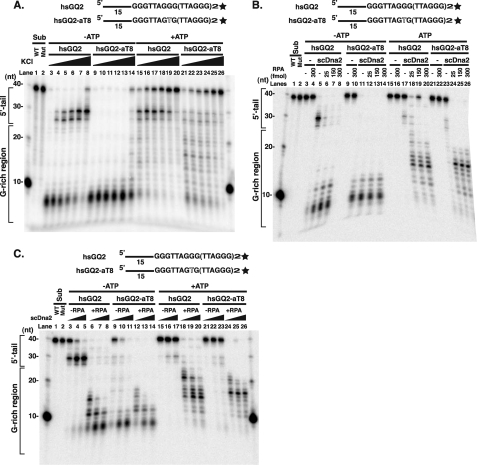
FIGURE 9.
scRPA stimulates scDna2 cleavage of G4 DNA. A, cleavage of intramolecular human telomeric G4 by scDna2. 3′ end-labeled hsGQ2 intramolecular G4 wild type hsGQ2 (15 fmol) and mutant hsGQ2-aT8 (30 fmol) were incubated with scDna2 (100 fmol) at KCl concentrations of 5, 15, 25, 35, 55, 105 mm (lanes 3–8, 9–14, 15–20, and 21–26) in the absence (lanes 3–14) and presence (lanes 15–26) of 2 mm ATP for 15 min at 37 °C, and nuclease products were analyzed by denaturing gel electrophoresis. Wild type hsGQ2 (lane 1) and mutant hsGQ2-aT8 (lane 2) substrate, without incubation, are also shown. Numbers shown on the left of the figure indicate the size of the markers. B, scRPA titrations show stimulation of scDna2 nuclease against intramolecular human telomeric G4. 3′ end-labeled hsGQ2 intramolecular G4 (5 fmol) and mutant hsGQ-aT8 (5 fmol) were preincubated on ice with indicated amounts of RPA in the absence (lanes 3–14) and presence (lanes 15–26) of 2 mm ATP. The nuclease reaction was started by adding scDna2 (100 fmol), and the reaction mixture was kept at 37 °C for 60 min. Nuclease products were then analyzed by denaturing gel electrophoresis. As a control, yDna2 was omitted from the reaction (lanes 3–4, 9–10, 15–16, and 21–22). Wild type (lane 1, WT) and mutant (lane 2, Mut) substrate were also loaded. C, scDna2 titration shows scRPA stimulates scDna2 nuclease against intramolecular human telomeric G4. 3′ end-labeled hsGQ2 intramolecular G4 wild type (5 fmol) and mutant hsGQ2-aT8 (5 fmol) were preincubated on ice in the absence (lanes 3–5, 9–11, 15–17, and 21–23) and presence (150 fmol, lanes 6–8, 12–14, 18–20, and 24–26) of scRPA. Increasing amounts of scDna2 (10, 50, and 100 fmol, as indicated by triangles) were then added to start the reaction, and the reaction mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. Nuclease products were analyzed by denaturing gel electrophoresis. hsGQ2 (lane 1) and hsGQ2-aT8 (lane 2) substrates, without incubation, are also shown.