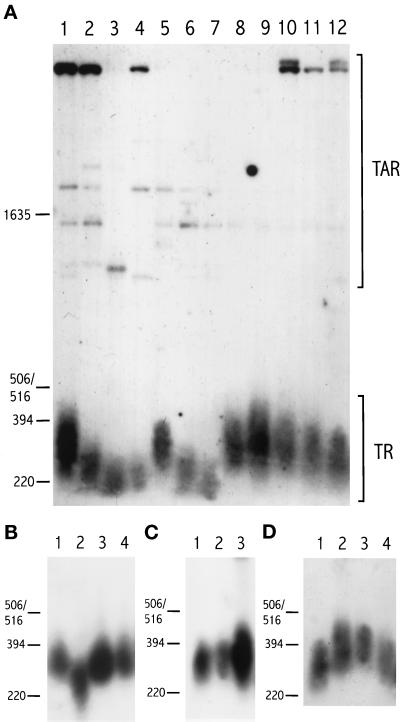
Figure 1.
Southern blot analysis of telomere length in different mutant and wild-type Sz. pombe strains. Cells were grown for ∼100 generations before harvest. Genomic DNA was restricted with ApaI and separated on 1.2% agarose gels. DNA was blotted to filters and probed with the 1.9-kb ApaI fragment of pEN42 (Nimmo et al., 1994). Positions of DNA size markers and their sizes in base pairs are given on the left. (A) Lane 1, strain 972h− (wild type); lane 2, h− rad1-1 ura4; lane 3, rad3-136 ura4 leu1; lane 4, NRC2341 (h−rad3-136); lane 5, rad9-192 ade6 ura4; lane 6, GK3 (rad17); lane 7, h− rad26::ura4+ leu1-32 ade6-704; lane 8, h− chk1::ura4+ leu1-32 ade6-704; lane 9, PR 87.97 (cdc2-1w); lane 10, cdc2-3w ura4 leu1 his3; lane 11, PGYQ686 (wee1::ura4+); lane 12, cdc25OP (adh:cdc25+). Brackets indicate the position of internal TAR and of the heterogeneous telomeric restriction fragment (TR). (B) Lane 1, 972h−; lane 2, h− rad26::ura4+; lane 3, hus1::LEU2; lane 4, cds1::ura4+. (C) Lane 1, 972h−; lane 2, NRC3242 (rad8-190); lane 3, NRC3239 (rad5). (The amount of DNA loaded in lane 3 is greater than in the other two lanes.) (D) Lane 1, 972h−; lane 2, NRC3241 (rad13); lane 3, NRC3240 (rad16); lane 4, rad21-45 ura4 leu1.