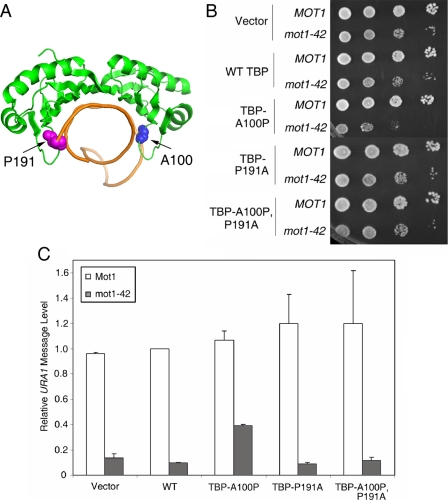
FIGURE 9.
A TBP allele with relaxed DNA binding polarity partially suppresses the requirement for Mot1 for URA1 transcription in vivo. A, schematic representation of the TBP-DNA complex (7) showing the positions of alanine 100 (blue spheres) and proline 191 (magenta spheres). These two residues disrupt the symmetry of the DNA binding surface and play a role in determining the binding orientation of TBP on promoter DNA (35). B, spot assay showing the synthetic growth defect in mot1-42 TBP-A100P cells. 10-Fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains were grown at 30 °C on synthetic media without leucine or tryptophan (for plasmid selection) for 2-3 days. C, quantitation of URA1 RNA levels, determined by Northern blotting, in MOT1+ and mot1-42 cells, with TBP alleles as indicated. Note the approximate 4-fold increase in RNA level in the mot1-42 TBP-A100P strain compared with the RNA level in mot1-42 cells only harboring wild-type TBP. Relative URA1 RNA levels were normalized to ACT1 in the same samples. Error bars are standard deviations from three sets of samples.