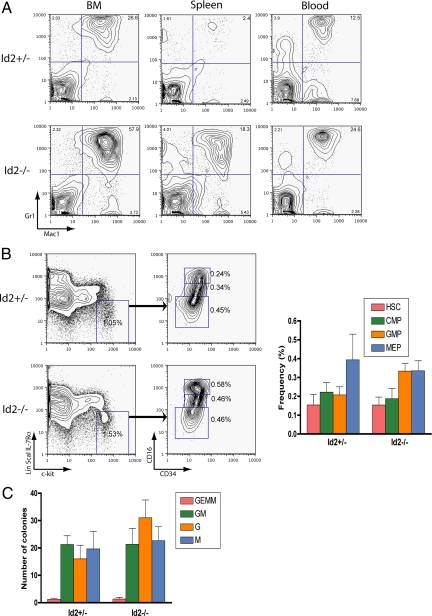
Fig. 1.
Increased neutrophil cellularity in Id2 deficient mice at 3–4 weeks after birth. (A) Bone marrow (BM), spleen, and peripheral blood derived from Id2 deficient mice show expanded myeloid population. Representative flow cytometric profile of hematopoietic cells isolated from bone marrow, spleen, and peripheral blood derived from Id2+/− and Id2−/− mice are shown. Cells were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled Mac-1 and phycoerythrin-labeled Gr-1. Note that percentages of Mac-1+Gr-1+ cells are markedly higher in Id2 deficient populations. (B) Effects of Id2 deletion on the numbers of hematopoietic progenitors in adult mouse BM. Total BM cells from Id2+/− and Id2−/− mice were harvested and prepared for analysis by flow cytometry. Shown are representative staining profiles for erythromyeloid progenitors (lin−/Sca-1−/IL-7Rα−/c-kit+) that were gated according to their expression of FcγR and CD34 to obtain the CMP, MEP, and GMP populations. Note the increased proportion of GMPs in the BM of Id2−/− mice. HSC refers to hematopoietic stem cell. CMP refers to common myeloid progenitor. GMP refers to granulocytic/monocytic progenitor. MEP refers to megakaryocytic/erythroid progenitor. (C) Total BM cells (2 × 104) from Id2+/− and Id2−/− mice were plated in methylcellulose-containing media supplemented with the appropriate cytokines for each progenitor type. Standard morphologic criteria were used to score colonies. GEMM refers to granulocyte/erythrocyte, macrophage/megakaryocyte colony-forming units. GM refers to granulocyte, macrophage colony-forming units. G refers to granulocyte colony-forming units. M refers to macrophage colony-forming units.