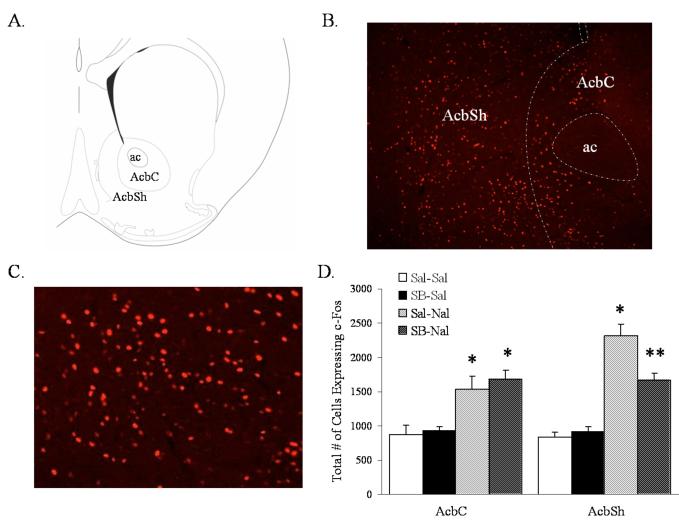
Figure 4.
Naloxone-induced morphine withdrawal results in the activation of Acb cells. SB-334867 attenuates naloxone-induced morphine withdrawal induction of c-Fos expression in the AcbSh. (A) Schematic anatomical representation of Acb subdivisions adapted from Paxinos and Franklin’s (49) Stereotaxic Atlas. Labeled areas delineate regions where c-Fos expression was examined. (B) Representative photograph illustrating c-Fos expression in the Acb of an animal pretreated with saline-naloxone. (C) Representative photograph of c-Fos expression in the AcbSh/AcbC boundary in higher magnification from the same animal presented in A. (D) Quantification of cells expressing c-Fos in the AcbC and AcbSh. Vertical lines represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Abbreviations used: AcbC, nucleus accumbens core; AcbSh, nucleus accumbens shell; ac, anterior commisure. * represents a significant naloxone effect (P<0.05). ** represents a significant naloxone interaction with SB-334867 (P<0.05).