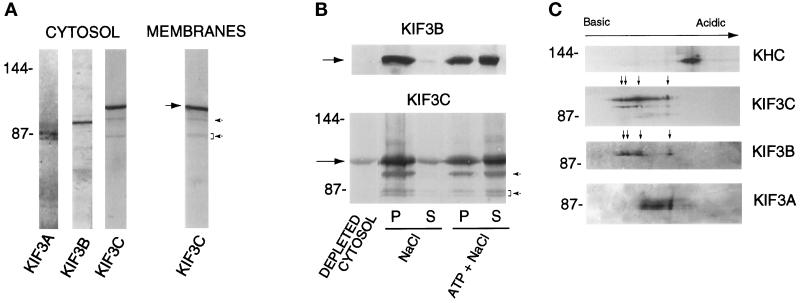
Figure 2.
Characterization of KIF3C protein. (A) KIF3C is both present in cytosol and associated with membranes. A 120,000 × g supernatant (cytosol) and membrane fraction were prepared from rat brain postnuclear supernatant. Samples of equal protein concentration were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies to KIF3A, KIF3B, and KIF3C. The large arrow points to KIF3C. Note that, similar to mouse KIF3A (Kondo et al., 1994), rat KIF3A is detected as a doublet in cytosol. (B) Nucleotide-dependent microtubule binding and release of cytosolic KIF3C protein. Rat brain cytosol was incubated with microtubules in the presence of 5 mM AMP-PNP. The mixture was separated by centrifugation into a supernatant (depleted cytosol) and a microtubule pellet. Microtubules were extracted with either 100 mM NaCl or 100 mM NaCl plus 7.5 mM ATP. Supernatants (S) and pellets of the extracted microtubules (P) were obtained by centrifugation. Equivalent volumes from each fraction were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-KIF3C and anti-KIF3B antibodies. Note that both KIF3C and KIF3B (arrows) are released by ATP and salt. Much less KIF3C and KIF3B are released by salt alone. (C) Isoelectric forms of KIF3C. A microtubule motor protein-enriched fraction obtained from rat brain cytosol was analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and Western blotting. Note the high number of charge variants of KIF3C compared with the other motor molecules tested (KHC, kinesin heavy chain). Arrows show the major charge isoforms in KIF3C and KIF3B. The positions of molecular size markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated at left. Note that the affinity-purified anti-KIF3C antibody also detects three minor polypeptides (arrowheads in A), which show nucleotide-dependent binding to and release from microtubules similar to KIF3C (arrowheads in B).