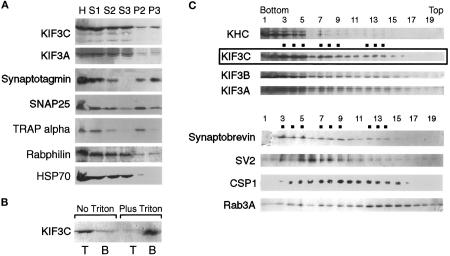
Figure 9.
Association of KIF3C with vesicle membranes. (A) Subcellular fractionation of rat brain homogenate by differential centrifugation. The homogenate (H), postnuclear supernatant (S1), 14,000 × g supernatant (S2) and pellet (P2), and 120,000 × g supernatant (S3) and pellet (P3) were probed for KIF3C, KIF3A, HSP70, and markers for various membrane compartments. Note that most of the membrane-associated KIF3C is found, together with the synaptic vesicle marker synaptotagmin, in the high-speed pellet (P3); a lower amount cofractionates with the medium-speed pellet (P2), enriched in endoplasmic reticulum (TRAP α) and synaptosomal plasma membrane (SNAP25). Also note that the cytosolic marker HSP70 is essentially absent from the P3 fraction. (B) Vesicle-bound KIF3C is solubilized by Triton X-100 extraction. Pelleted brain membranes were resuspended in buffer without or with Triton X-100 and separated by flotation from residual cytosolic proteins (left lanes) or detergent-solubilized proteins (right lanes). T and B are top (membrane) and bottom fractions after flotation. (C) Cofractionation of KIF3C with rat brain vesicles. A crude membrane fraction depleted of heavy membranes (see MATERIALS AND METHODS) was fractionated by flotation through a Nycodenz gradient. Samples from each fraction were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of motor molecules and various vesicle markers. The broad distribution of the markers is typical for this type of vesicle fractionation. Note that the distribution of KIF3C partially overlaps with that of several synaptic vesicle membrane proteins, but most resembles that of synaptobrevin. Dots indicate peaks in the distribution of KIF3C and synaptobrevin. KHC, kinesin heavy chain.