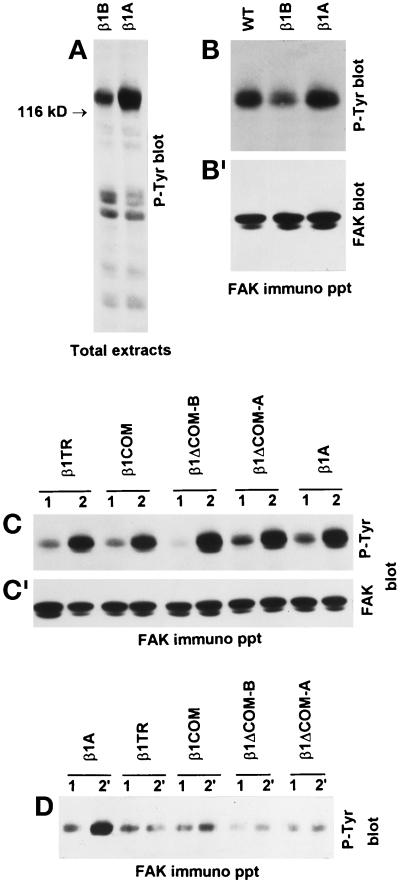
Figure 10.
Inhibition of β1A-induced FAK tyrosine phosphorylation by β1B expression. To specifically trigger tyrosine phosphorylation of intracellular proteins mediated by the the endogenous or transfected β1 integrins, cells were plated on plastic dishes coated with the anti-hamster β1 mAb 7E2 (A–C) or with the anti-human β1 mAb TS2/16 (D), respectively. (A and B) Tyrosine phosphorylation of total cellular proteins (A) and FAK (B) induced by endogenous hamster β1A was detected by Western blotting with anti-phosphotyrosine mAb PY20. Note reduced tyrosine phosphorylation of 116- to 130-kDa proteins (A) and FAK (B) in β1B-transfected CHO cells. (B′) The reprobing of the blot with FAK antibodies is shown. (C) The tyrosine phosphorylation of FAK via endogenous β1A was also evaluated in CHO cells expressing the different cytoplasmic domain mutants. Cells were plated on poly-l-lysine (lanes 1) for control and on 7E2 mAb to endogenous hamster β1 (lanes 2). (C′) The reprobing of the blot with FAK antibodies is shown. (D) The ability of the different mutants to trigger FAK tyrosine phosphorylation directly was evaluated by plating cells on mAb TS2/16 to the transfected human β1 (lanes 2′) or poly-l-lysine as control (lanes 1).